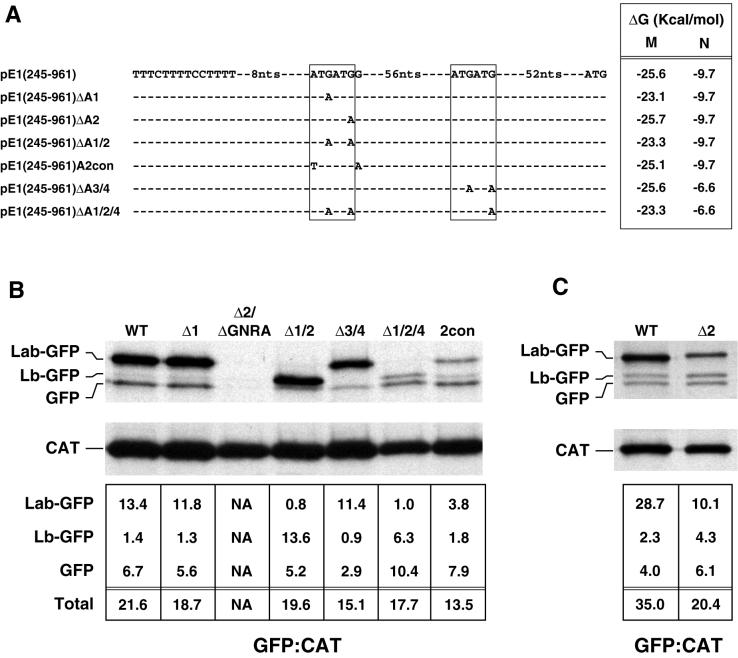
FIG. 5.
Identification of functional ERAV AUG codons by mutational analysis. (A) Representation of ERAV sequence surrounding the ATG codons (boxed) downstream of the polypyrimidine tract (indicated to the left of the sequence) in a wild-type ERAV vector, pE1(245–961), and in derivatives of this vector. These derivatives contain point mutations at the positions shown. The minimum free energy M and N stem-loops predicted in each mutant are shown on the right. Plasmid names are given at the extreme left. (B) RIP of vTF7-3-infected BHK-21 cell extracts following transfection with ERAV mutant plasmids and metabolic labeling with [35S]methionine. Extracts were immune precipitated with a mixture of GFP and CAT antibody-coated protein A beads. The lanes are labeled with shortened plasmid names. The WT lane represents the parental pE1(245–961) plasmid containing the wild-type IRES, while the Δ2/ΔGNRA lane represents pE1(245–961)Δ2/ΔGNRA, a plasmid that contains a PCR-induced mutation in the GNRA tetraloop (converting it to GNRG) in addition to the AUG2 mutation. The intensities of the bands were determined by phosphorimager analysis, and the  ratio was determined for each GFP band following correction for methionine content (bottom). (C) Results of an experiment similar to that in panel B, but using the pE1(245–961)Δ2 mutant.
ratio was determined for each GFP band following correction for methionine content (bottom). (C) Results of an experiment similar to that in panel B, but using the pE1(245–961)Δ2 mutant.