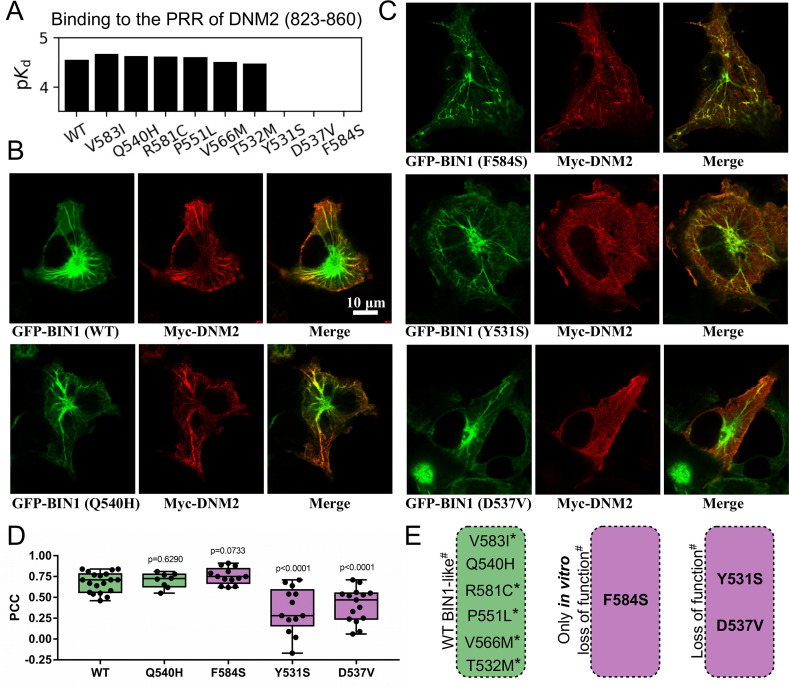
Figure 2. Several BIN1 variants of unknown clinical significance have a strong impact on the binding of DNM2 and display altered cellular phenotype.
(A) Measured affinities of the PRR of DNM2 against a set of natural BIN1_SH3 variants. Most variants interact with DNM2 with similar affinities, but Y531S, D537V and F584S variants disrupt this interaction. Affinities are expressed as negative logarithm of dissociation constants, i.e. pKd 4 equals to 100 μM Kd. (B) Membrane tubulation assay performed with WT BIN1 and DNM2, as well as Q540H variant which binds DNM2 with the same affinity as WT BIN1. (C) Membrane tubulation assay performed with the variants displaying decreased affinities to DNM2. Cos-1 cells were transfected with GFP-BIN1 and Myc-DNM2. The effect of F584S seems to be apparently rescued in the context of FL BIN1, but both Y531S and D537V variants are unable to efficiently recruit DNM2 to membrane tubules in cells. (D) Statistical analysis of single-cell co-localization experiments between the BIN1 variants and DNM2 (n[WT]=19, n[Q540H]=8, n[F584S]=13, n[Y531S]=13, n[D537V]=15). P values were calculated between Pearson correlation coefficients (PCC) of WT and missense variants using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s T-test. Box plots indicate the median and upper and lower quartiles, and whiskers label the minimal and maximal measured PCC values. Individual data points representing measurements of single cells are also indicated. (E) A summary of the effects of the BIN1 variants. Asterisk indicates that the variants were only tested in vitro, and # indicates that the effects were measured based on the BIN1-DNM2 interaction phenotype. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for additional images.