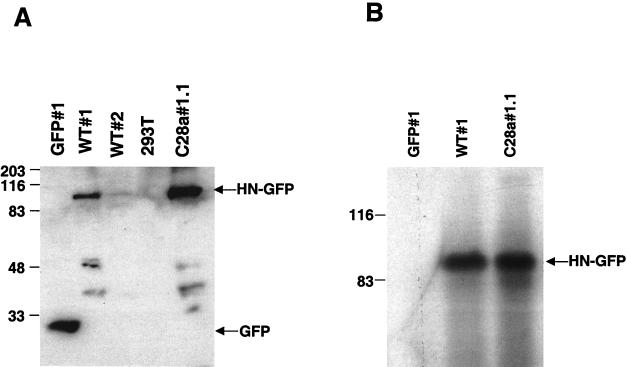
FIG. 2.
(A) Western blot analysis of the selected clones using anti-GFP antibodies for detection. Cell lysates containing identical quantities (50 μg) of protein per lane and control were probed with anti-GFP polyclonal antibodies. The lysates are from the cells indicated above the lanes. The 90-kDa band corresponds to the wild-type HN-GFP protein, expressed in different amounts in WT#1 and WT#2. The lower molecular mass bands likely represent degradation products of HN-GFP. (B) Immunoprecipitation of proteins from HN-GFP-expressing cells and control GFP-expressing cells. Cell extracts containing equal amount of protein from WT#1, C28a#1.1, and GFP#1 were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-HPF3 serum. The precipitated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE in 11% gels, transferred to a Zetabind membrane by electroblotting, and immunoblotted with anti-HPF3 serum. The lysates are from the cells indicated above the lanes. The 90-kDa band corresponds to the expected molecular weight of the HN-GFP fusion protein.