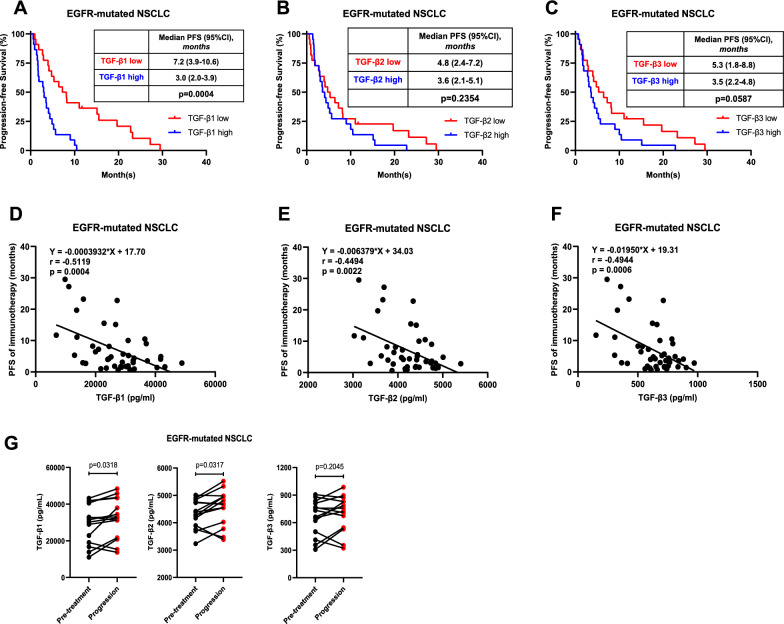
Fig. 6.
TGF-β was a potential therapeutic predictor for the immunotherapy effect in EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients. A–C Kaplan–Meier analysis of PFS probability in EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients who had undergone immunotherapy. The patients were stratified according to high versus low levels (cutoff, median) of circulating TGF-β1 (A), TGF-β2 (B), or TGF-β3 (C) at the baseline of immunotherapy measured by the Luminex assay. D–F Correlation analyses of immunotherapy PFS and circulating TGF-β1 (D), TGF-β2 (E), or TGF-β3 (F) levels. G Circulating TGF-β1, TGF-β2, and TGF-β3 levels were measured in EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients stratified by prior to immunotherapy or after progression of disease. The log-rank test was used to calculate P values in A–C. The Spearman's rank correlation coefficient test was used in D–F. Student’s 2-tailed unpaired t test was used for 2-group comparisons in G