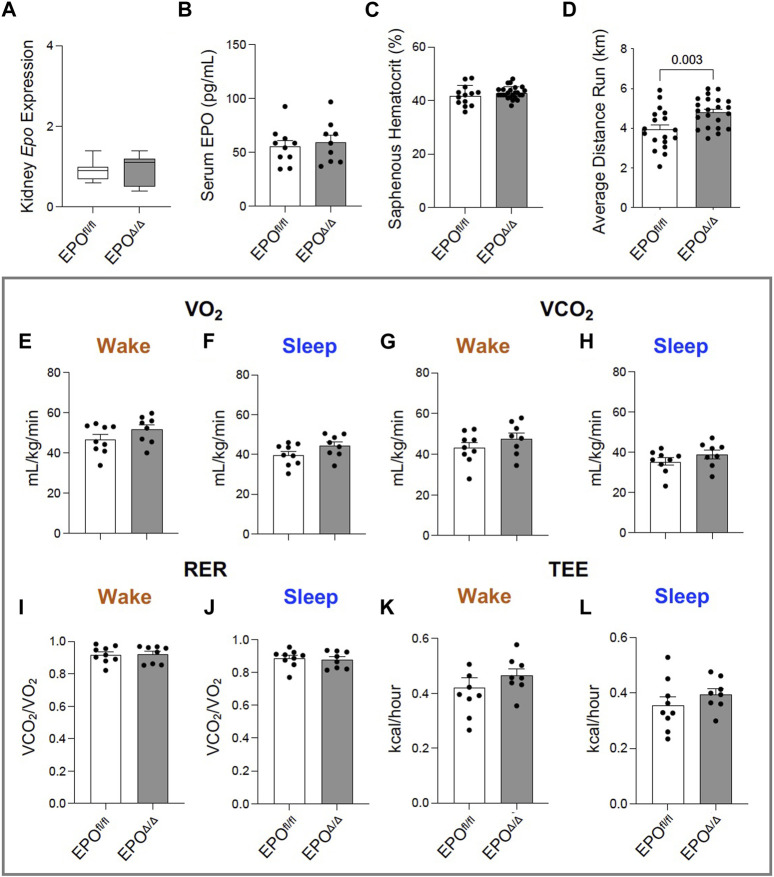
FIGURE 2.
Greater voluntary wheel running capacity in EPOΔ/Δ compared to EPOfl/fl mice occurred independent from differences in hematocrit and whole-body metabolism. (A) Kidney Epo RNA expression (normalized to β-Actin) in EPOfl/fl and EPOΔ/Δ mice, (B) serum EPO, (C) hematocrit (%) collected from the saphenous vein of EPOfl/fl and EPOΔ/Δ mice, and (D) average voluntary wheel running distance (km) across 3 days. Comprehensive Laboratory Animal Monitoring System (CLAMS) measured (E, F) VO2 (mL/kg/min), (G, H) VCO2 (mL/kg/min), (I, J) RER (VCO2/VO2), and (K-L) total energy expenditure (TEE, kcal/hour) in EPOfl/fl and EPOΔ/Δ mice during their sleep and wake phases. An unpaired, two-tailed t-test was used to detect differences. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (for qPCR, serum EPO levels, and hematocrit) or mean ± SEM (for average running distance and whole-body metabolic readings). Data were considered significant when p < 0.05.