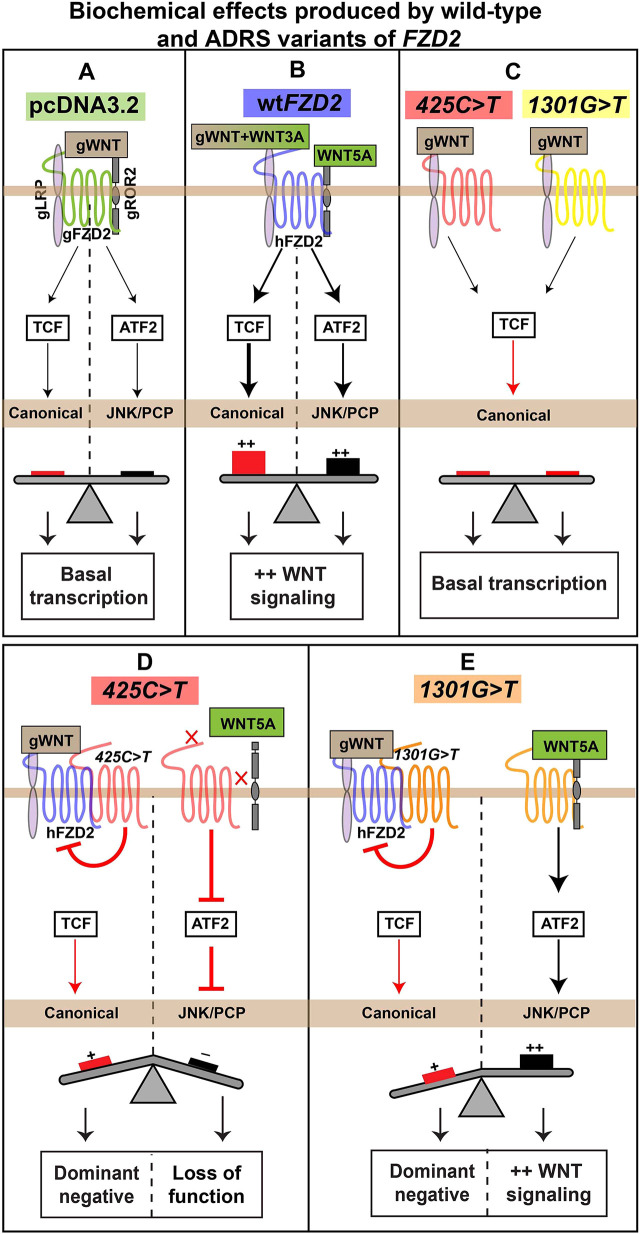
Fig. 8.
Summary of signaling effects produced by wild-type hFZD2 or hFZD2 variants. Schematic of biochemical activity of wild-type or variants of hFZD2. (A) Transfection of the empty vector (pcDNA3.2) in frontonasal mass mesenchyme or HEK293T cells showed basal level activity in both the canonical (Super TOPFlash reporter or STF, red) and JNK/PCP (ATF2 reporter, black) pathways. (B) Wild-type hFZD2 (blue) significantly activated STF and ATF2. (C) The 425C>T (red) and the 1301G>T (yellow) variants weakly activated STF. (D) The 425C>T variant, when combined with wild-type hFZD2, showed a dominant-negative effect on the activity of the wild type. When 425C>T was combined with WNT5A or mRor2, the JNK/PCP pathway was not activated. (E) The 1301G>T variant also, when combined with wild-type hFZD2, showed a dominant-negative effect. The 1301G>T variant by itself and combined with WNT5A and mRor2 activated the JNK/PCP pathway to the same extent as wild-type hFZD2. ADRS, autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome.