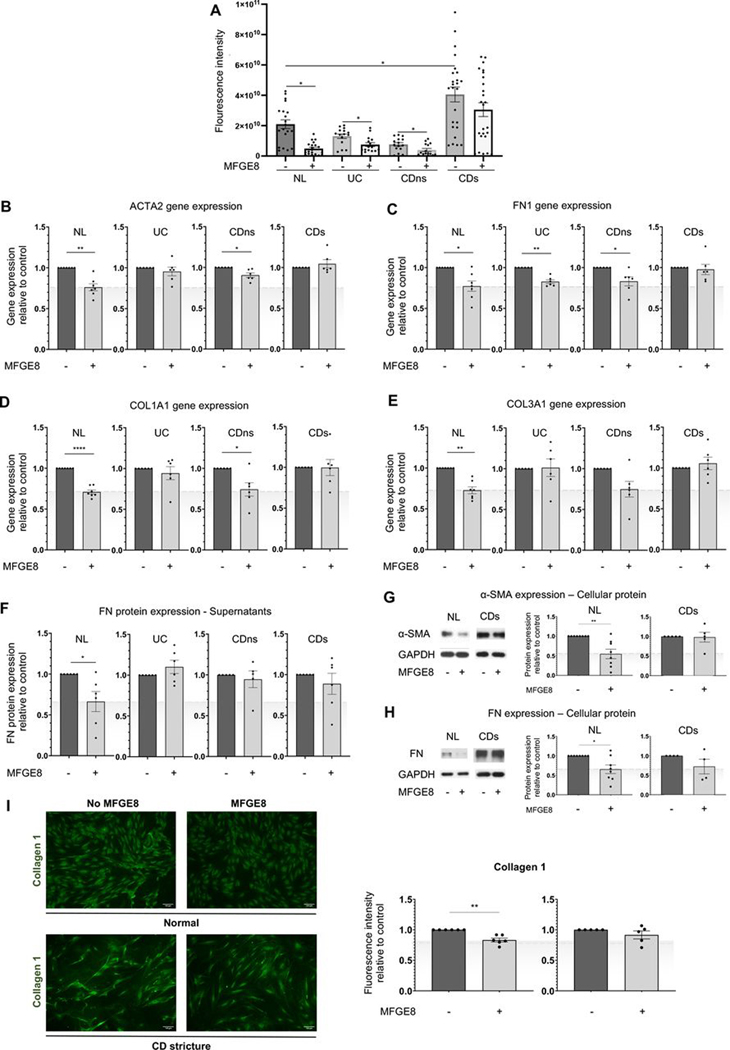
Figure 4.
Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 (MFGE8) shows antifibrotic effects on primary human intestinal myofibroblasts (HIMFs) derived from normal (NL) but not patients with stricturing Crohn’s disease (CD). Primary HIMFs were isolated from freshly resected intestinal tissues from NL, UC, non-strictured CD (CDns) and strictured CD (CDs). (A) Deposition of fibronectin (FN) was measured using an extracellular matrix deposition assay. An increase in FN deposition was noted at baseline between the CDs HIMF and all other phenotypes. On exposure to MFGE8, NL, UC and CDns HIMF reduced FN, but CDs did not (n=3–5 cell lines per group with 5 independent experiments per line). (B–F) NL HIMF exposed to MFGE8 reduced gene expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, ACTA2), FN (FN1), collagen I (COLI, COL1A1), COLIII (COL3A1) and FN protein. CD HIMF did not show any response to ACTA2, FN1, COLA1A1 and COL3A1 gene expression by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and FN protein by ELISA. HIMF UC only reduced FN1 gene expression, and CDns reduced ACTA2, FN1 and COL1A1 gene expression in response to MFGE8 (n=5–7 per group). (G–I) HIMF NL reduced cellular protein expression of α-SMA and FN (immunoblot) and COLI (immunocytochemistry), which was not observed in HIMF CDs (n=4–8). *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ****, p<0.0001. α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; CDs, strictured CD; CDns, non-strictured CDns; COL, collagen; FN, fibronectin; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase;MFGE8, milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8; NL, normal.