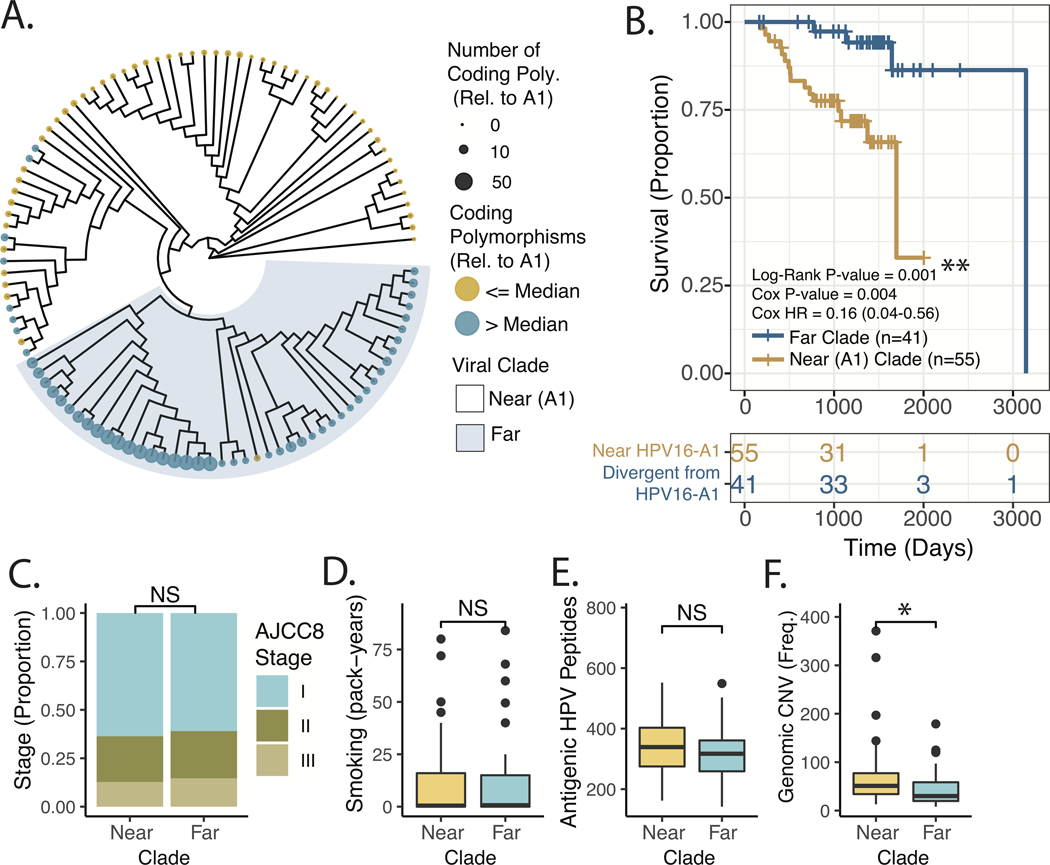
Figure 4. Tumor Genomic and Patient Factors Stratified by Maximum Parsimony Phylogeny of OPSCC HPV16 Viral Genomes.
A. Maximum Parsimony Phylogeny of HPV16 genomes. Color – Above or below the median number of non-synonymous clonal polymorphisms in the HPV16 genome relative to the A1 reference sequence. Tip point size/color – Total number of non-synonymous clonal polymorphisms in the HPV16 genome relative to the A1 reference sequence. B. Kaplan-Meier Plot of Recurrence-free Survival, comparing viral clades indicated in Panel A. Log-Rank P-value – p-value derived from the Log-Rank test. Cox P-value – the p-value derived from a univariate Cox Model. Cox HR – estimated hazard ratio with 95% confidence interval derived from Cox Model. C. Proportion of Cases Stratified by AJCC8 Clinical Staging in near and far clades. Significance based on chi-squared test. D. Tobacco Smoke Exposure for near and far clades. Significance based on Wilcoxon Rank-sum test. E. Predicted Viral Proteomic Neo-Antigenicity for near and far clades. Neo-Antigenicity was estimated by the number viral peptides with <350nM affinity for MHC, based on the patients HLA subtype (see methods for further description). Significance based on Wilcoxon Rank-sum test. F. Human Genomic Copy-number Variant Burden. Number of copy number events as identified by the SynthEx pipeline. Significance based on Wilcoxon Rank-sum test. * P-value < 5*10^−2.