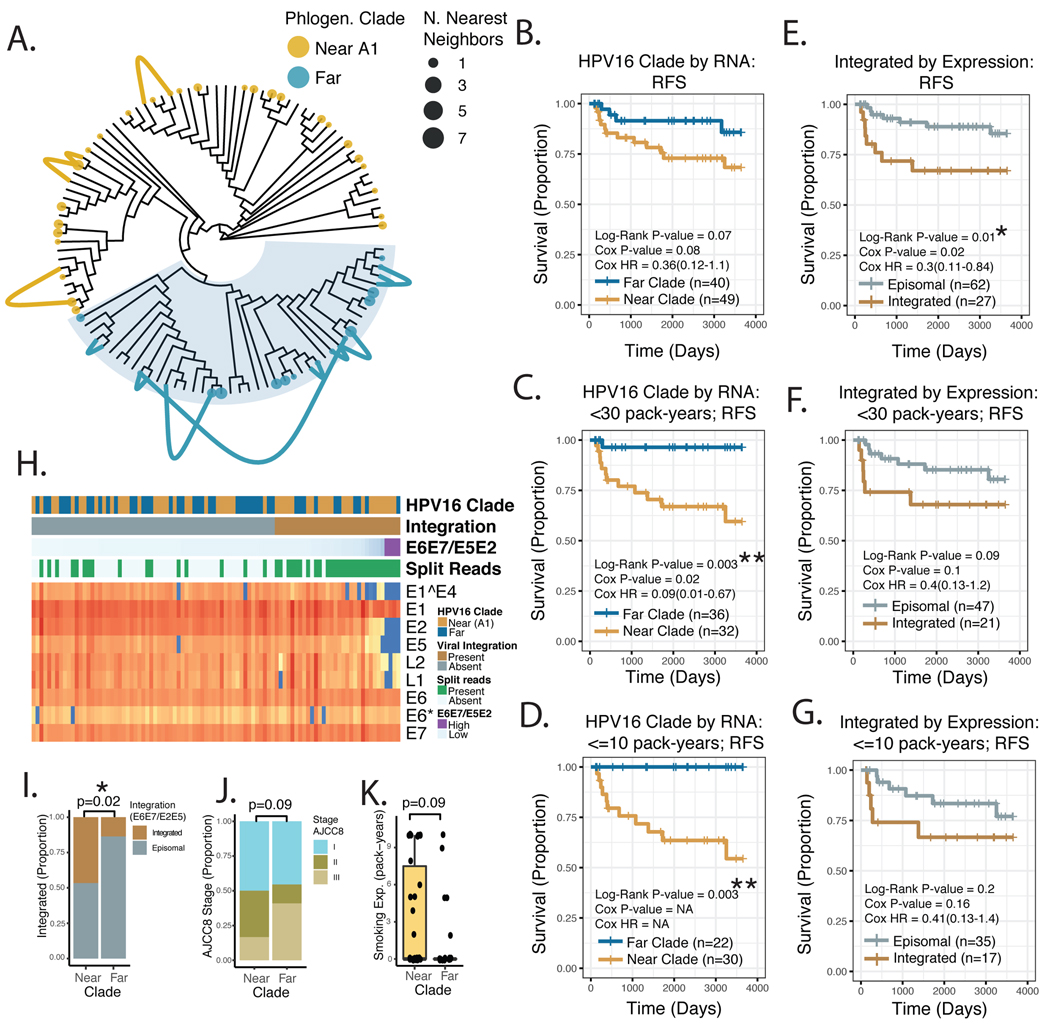
Figure 6. HPV16 Viral Genotyping and Integration Analysis by RNA Sequencing.
A. Maximum Parsimony Phylogeny of HPV16 genomes from the DNA sequencing cohort. Links – Connect known (DNAseq) genotype, with nearest neighbor genotype assigned from RNAseq, for 13 patients with available DNA and RNA sequencing data. Color –Viral clade as assigned in Figure 4. Tip point size – Number of RNAseq cases assigned at a neighbor to the indicated DNAseq case. B-G. Kaplan-Meier Plot of Recurrence-free Survival, comparing viral clades vs. viral integration status, stratified by tobacco smoke exposure. Log-Rank P-value – p-value derived from the Log-Rank test. Cox P-value – the p-value derived from a univariate Cox Model. Cox HR – estimated hazard ratio with 95% confidence interval, from Cox Model. NA – Cox proportional hazard modeling was not possible due to no events (measurable hazard) in one of the two groups. H. Annotated heat map of HPV16 viral gene expression. Columns – tumor samples, organized by E6E7/E5E2 ratio. Viral Clade – as assigned in panel A. Integrated – Assigned integration status based in E6E7/E5E2 ratio. Split Reads – Presence of detectable split read-pairs mapping to both the HPV16 and human genome. I-K. Genomic and clinical features of the <= 10 pack-year smoking exposure sub-group. I. HPV16 Integration status - based in E6E7/E5E2 ratio Significance based on Chi-squared test. J. AJCC8 summary stage. Significance based on Chi-squared test. K. Tobacco Smoke Exposure. Significance based on Wilcoxon Rank-sum test. * P-value < 5*10^−2. NS – not significant. Near – HPV16 viral clade nearest to the HPV16-A1 sub-lineage based on JC69 distance. Far – HPV16 viral clade distal to the HPV16-A1 sub-lineage based on JC69 distance.