FIGURE 2.
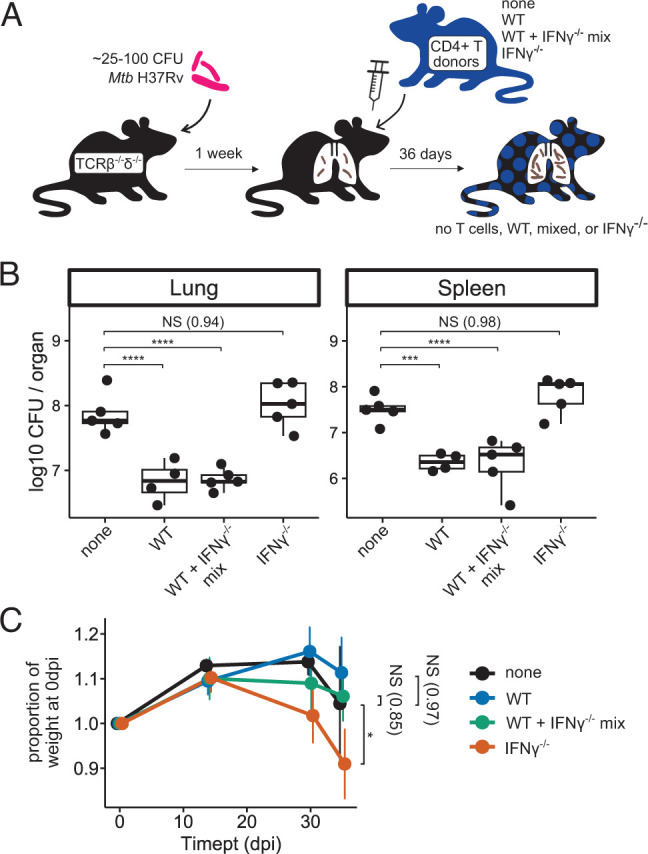
Adoptively transferred IFN-γ−/− CD4+ T cells do not reduce Mtb burden, and they exacerbate disease in TCRβ−/−δ−/− mice. (A) Schematic of adoptive transfer of zero (none) or 3 × 106 WT, 50%/50% mixed WT+IFN-γ−/−, or IFN-γ−/− CD4+ T cells to T cell–deficient host mice postinfection with aerosolized Mtb. (B) Bacterial burden in lungs and spleens of Mtb-infected adoptive transfer mice at 36 dpi. Results are representative of two independent experiments. (C) Weight trends of Mtb-infected adoptive transfer mice through 36 dpi. Statistical significance is shown for weights at 36 dpi. n = 5 none, n = 4 WT, n = 5 WT+IFN-γ−/−, and n = 5 IFN-γ−/− adoptive transfer mice. Results are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Dunnett’s test using “none” as the control group. *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.
