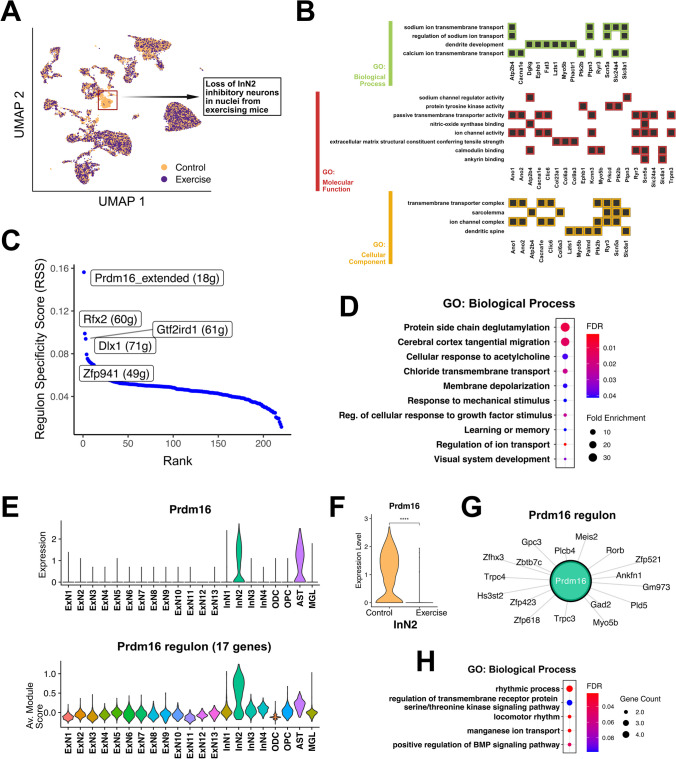
Fig. 2.
Selective loss of InN2 inhibitory neuron cluster upon exercise indicates a role of the transcription factor Prdm16. A UMAP plot with cells colored by the experimental group, showing the loss of InN2 inhibitory neurons upon exercise. B Heatmap plots of functional annotation for specific genes among the top 50 markers of the InN2 cluster that had significantly enriched GO (biological process, molecular function, and cellular component) terms. C Cell-type specific regulons for InN2 cluster identified using the SCENIC workflow. The y-axis denotes the regulon specificity score (RSS) (with high RSS values indicating high cell-type/cluster specificity, and vice versa). The x-axis denotes the rank of each regulon within the selected cluster, based on the RSS. The top 5 ranked regulons for InN2 are labeled on the plot, with the number of genes comprising each regulon indicated within parentheses. (Regulons ending with “extended” also include motifs linked to the transcription factor by lower confidence annotations). D Dot plot showing significant GO biological process terms enriched among the collective list of genes and transcription factors (TFs) making up the top 5 regulons, as indicated in the RSS-Rank plot in (C). E Violin plots depicting the normalized expression of Prdm16 (top panel), and the average module score (expression) for the genes included in the Prdm16 regulon (bottom panel) in all clusters. F Violin plot showing the expression of Prdm16 in the InN2 cluster, split between exercise and control cells. G Network plot showing the 17 genes comprising the Prdm16 regulon. H Dot plot showing significant GO biological process terms enriched among the list of 17 Prdm16 regulon genes