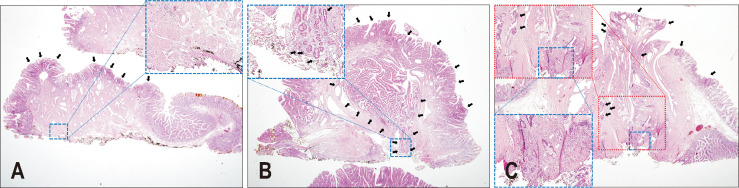
Fig. 2.
Representative histologic images of tubular adenomas with resection marginal status of endoscopic papillectomy specimens (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×10). Tubular adenoma with (A) a negative margin. Dysplastic cells (black arrows) are on the duodenal mucosal surface. Blue inset: medium-power magnification (×40) of the deep resection margin (black ink). No dysplastic cells were present on the margin. Tubular adenoma with (B) a positive margin. Dysplastic cells (black arrows) were continuously present on the duodenal mucosal surface, intra-ampulla, and deep resection margin (black ink). Blue inset: medium-power magnification (×40) of the deep resection margin (black ink). Tubular adenoma with (C) an indeterminate resection margin. Dysplastic cells (black arrows) were discontinuously present on the duodenal mucosal surface and intra-ampulla. Similar atypical cells with nuclear elongation were present on the deep resection margin (black ink). However, thermal artifacts (white arrows) led to nuclear pseudo-elongation, which prohibited differentiating with true dysplastic cells on the resection margin. Red inset: medium-power magnification (×40) of the deep resection margin (black ink). Blue inset: high-power magnification (×100) of the deep resection margin in the red inset (black ink).