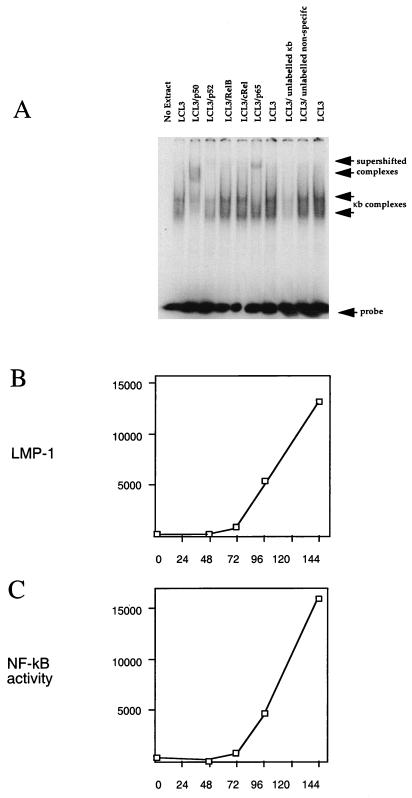
FIG. 8.
(A) Establishment of specificity of gel retardation assay for NF-κB complexes with LCL3 cell extracts by competition with 100-fold excess of unlabelled NF-κB oligonucleotide or a control oligonucleotide of unrelated sequence. NF-κB complexes (arrows) were also tested in supershift assays with antibodies to p50, p52, RelB, cRel, and p65 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology antibodies sc-114, sc-848, sc-226, sc-70, and sc-109, respectively) as indicated (1 μg per assay). (B) Purified B cells positively selected from peripheral blood were infected with EBV in a time course (hours post infection), and aliquots were assayed by Western blotting for LMP-1. The LMP-1 signal was quantified by scanning the autoradiograph, and the results are plotted in arbitrary units. (C) Nuclear extracts were prepared from the same time course of infection as for panel B and used in a gel retardation assay for NF-κB performed as for panel A. The active NF-κB, indicated by the amount of specifically shifted probe, was quantified by scanning the autoradiograph, and the results are plotted in arbitrary units.