Figure 5:
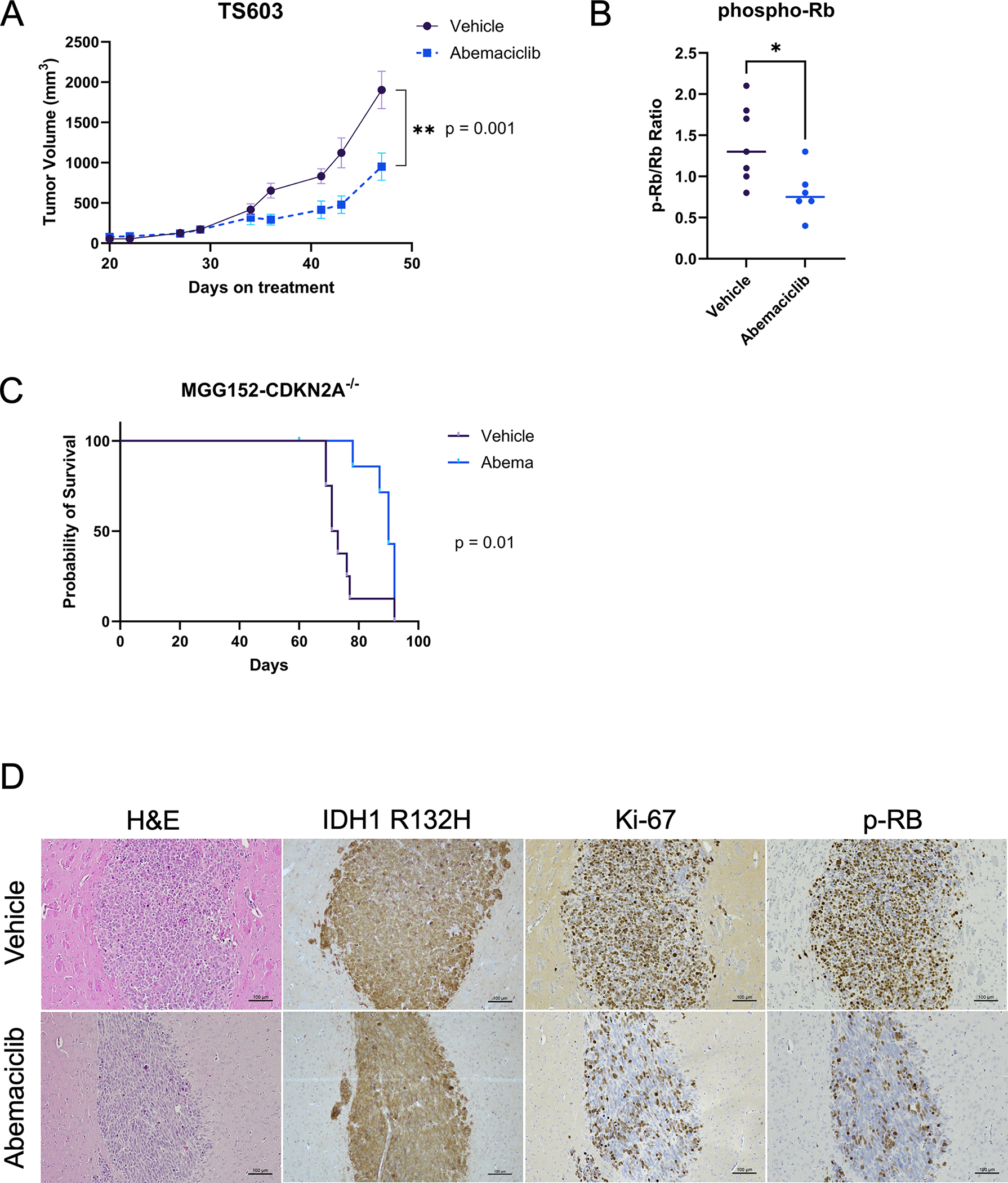
Abemaciclib slows tumor growth in IDH-mutant glioma models with CDKN2A deletion. (A) Tumor volumes of TS603 subcutaneous xenografts in animals treated with abemaciclib (N = 6) or vehicle control (N = 7) five times per week. Bars ± SEM. (B) Ratio of phospho-Rb to total Rb detected in each tumor taken at study endpoint show reduction to a mean of 0.8 in abemaciclib treated tumors compared to 1.4 for vehicle treated tumors. Comparison based on unpaired t-test, p = 0.02. (C) Survival curve of mice bearing intracranial xenografts of MGG152-CDKN2A−/− sgRNA3 treated five times per week with abemaciclib (N = 8) or vehicle (N = 8). One animal in Abemaciclib group censored due to unrelated dermatologic issue. (D) Representative images of immunohistochemistry of tumors extracted from vehicle or abemaciclib-treated animals, showing IDH1 R132H, Ki-67 and phosphorylated Rb (p-Rb).
