Figure 1.
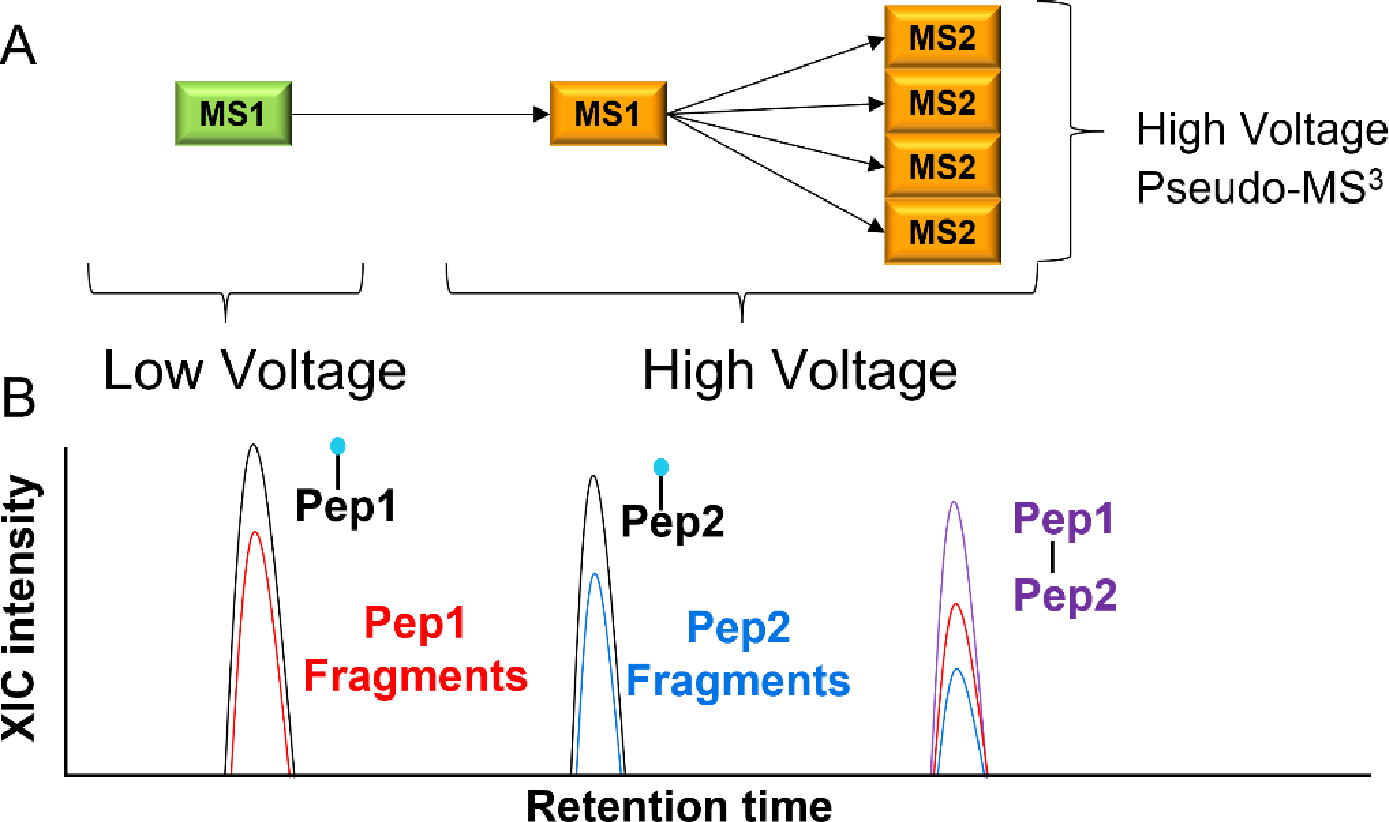
In-source fragmentation data acquisition cycle and search strategy. (A) In an in-source experiment for crosslink detection, the declustering and/or desolvation source voltage setting is initially set at a typical value for the first high-resolution scan, to support the detection of the intact crosslinked peptide. In a second high-resolution scan, this source voltage is quickly increased to fragment the crosslinker for mass measurement of the component peptides. Subsequent MS2 scans are performed at this elevated voltage to sequence the resulting fragmented peptides. (B) The peptides identified at the high source voltage setting are linked back to a potential crosslinked peptide using accurate masses from both MS1 scans. The figure shows that chromatographic separation is required to resolve potential interferents.
