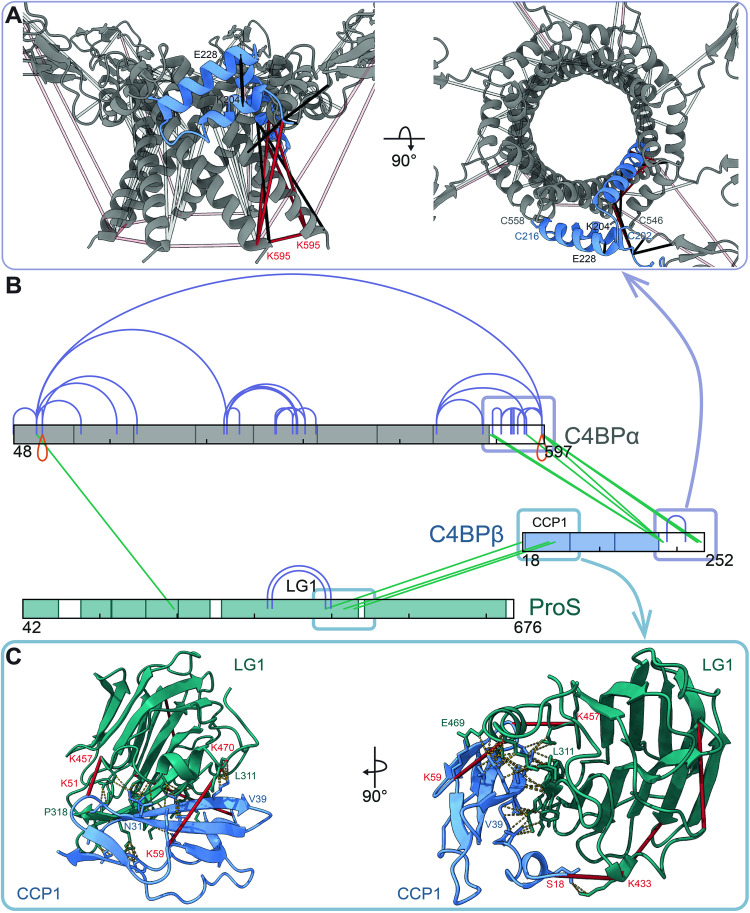
Figure 3. Cross-linking mass spectrometry highlights interaction interfaces of the C4BP assembly.
(A) The structural model of the α7β1 core displays seven C4BPα (gray) with C4BPβ (blue) inserted in a helix-hairpin-helix conformation with detected DMTMM (black) and DSS (red) cross-links. To highlight C4BPβ involving restraints, C4BPα intra-protein cross-links (except for the K595 self-link) are visualized as semi-transparent. Visualized were the shortest possible cross-links with an allowed 2 Å difference. (B) An overview of the observed XL-MS restraints. XL-MS revealed C4BPβ CCP1 interaction with LG1 of ProS and highlighted the assembly of C4BPα and C4BPβ at the C-terminus of both chains. Intra- (purple), inter- (green), and self- (orange) cross-links of C4BPα (gray), C4BPβ (blue), and ProS (teal) are color-annotated. Visualized were cross-links detected in two out of three experimental replicates. (C) The proposed C4BPβ–ProS interface. The structural model highlights interactions between the C4BPβ CCP3 (blue) and the ProS LG1 (teal) with the DSS cross-links (in red) and resulting interacting residues connected by yellow dashed lines. The generation of the structural models is described below in the full-length glycosylated models of the C4b-binding protein section. Source data are available online for this figure.