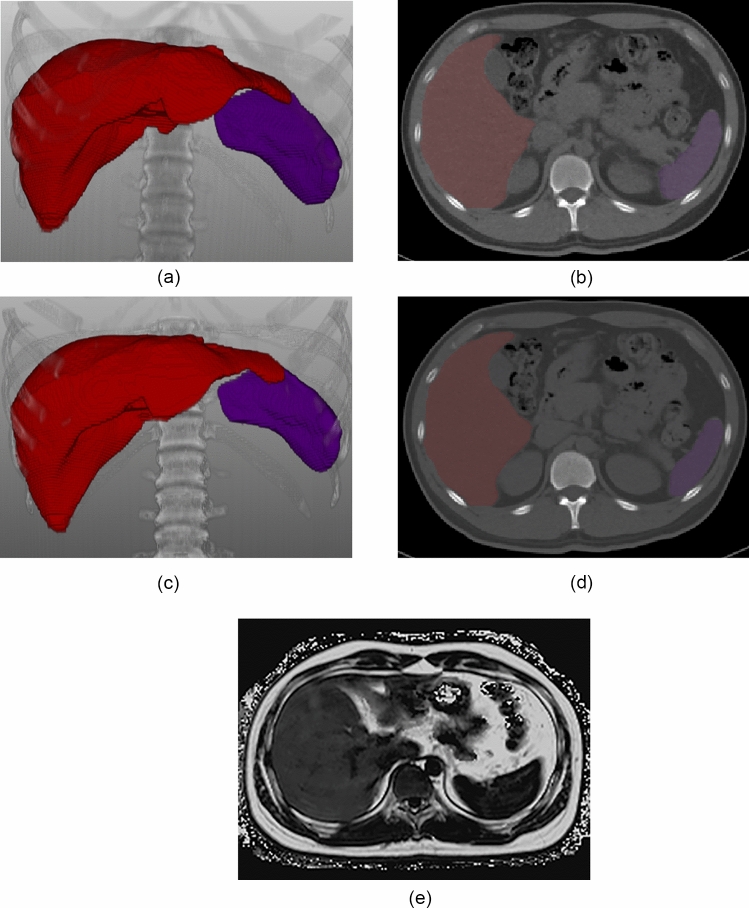
Fig. 2.
An illustration of volumetric CT attenuation measurement of the liver and spleen in a 27-year-old man with hepatic steatosis. Fully-automated organ segmentation was performed for the liver and spleen on virtual non-contrast (VNC) CT scan (a: 3D volume rendering image, b: axial image) and true non-contrast (TNC) CT scan (c: 3D volume rendering image, d: axial image), respectively. Volumetric measurements of CT attenuation values were as follows: LVNC = 48.3 HU, SVNC = 47.0 HU in VNC imaging; LTNC = 44.4 HU, STNC = 49.2 HU in TNC imaging. Accordingly, LAIVNC was 1.3 HU and LAITNC was -4.8 HU. Hepatic steatosis was confirmed with an MRI-PDFF value of 14.8% (e: MRI-PDFF map). MRI-PDFF = magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction; L = volumetric mean CT attenuation values of the liver; S = volumetric mean CT attenuation values of the spleen; LAI = liver attenuation index, defined as L minus S