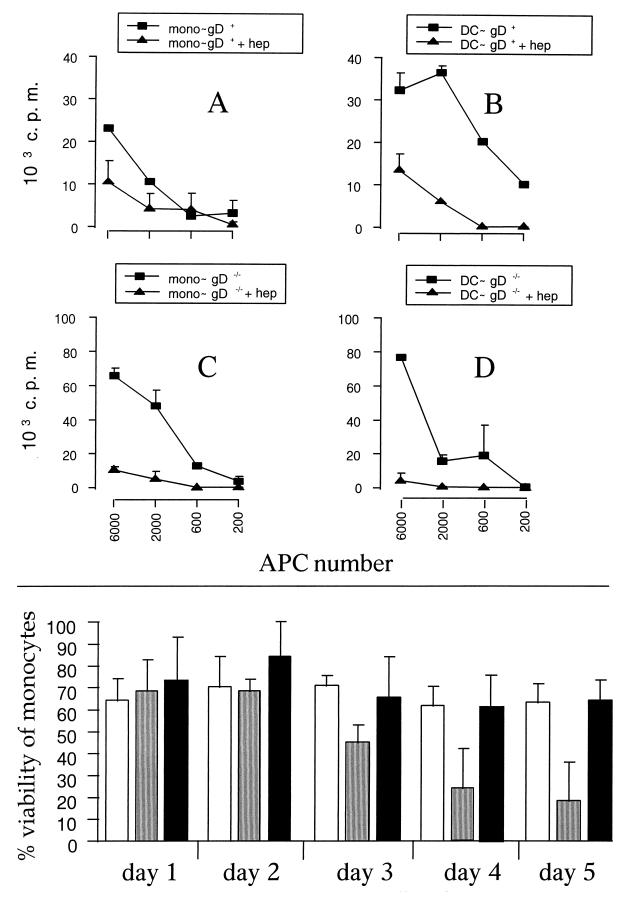
FIG. 5.
(Upper panel) The interaction of BHV-1 with cell membrane through the gD glycoprotein is dispensable for efficient antigen presentation, while attachment is necessary. CD2+ T lymphocytes were cultured with increasing numbers of APC infected with gD+ (recombinant strain 8221) (A and B) or gD−/− (BHV-1/80-221) BHV-1 strains (C and D). The viruses were left untreated (closed squares) or pretreated (closed triangles) with 500 U of soluble heparin/ml for 15 min at 37°C and added to APC for 1 h. Proliferation was assessed by thymidine incorporation during the last 10 h of 5 days of culture. The data are expressed as counts per minute (c.p.m.), and each point represents the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate cultures. The results are representative of three independent experiments. (Lower panel) gD−/− does not reduce the viability of monocytes, in contrast to wild-type BHV-1. Monocytes were either mock infected (open bars) or incubated with live wild-type BHV-1 (shaded bars) or with gD−/− deletion mutant (black bars) at an MOI of 1. The monocytes were harvested at different days after treatment, and the percentage of viable cells was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The results represent the percentage of dead/dying cells (mean ± standard deviation of five randomly selected fields), as determined by the number of calcein AM-positive cells/number of calcein AM and EthD-1-positive cells.