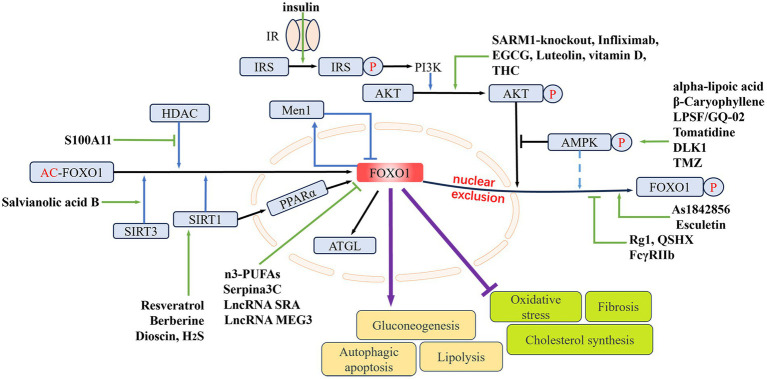
Figure 2.
The regulating role of FOXO1 in MAFLD. The nuclear expression of FOXO1 is mainly determined by its phosphorylation and acetylation levels. Phosphorylation of FOXO1 by p-AKT and p-AMPK can lead to its nuclear exclusion. The deacetylases HDAC, SIRT1, and SIRT3 can deacetylate FOXO1, thereby upregulating its nuclear expression. Elevated FOXO1 expression can promote hepatic gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and hepatocellular autophagy and apoptosis, while inhibiting hepatic oxidative stress, fibrosis, and cholesterol synthesis. Different drugs or genes can directly or indirectly influence nuclear FOXO1 expression, thereby modulating MAFLD. IR, insulin receptor; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; Men1, menin 1; HDAC, histone deacetylase; SIRT1/3, sirtuin 1/3; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; THC, tetrahydrocurcumin; EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate; DLK1, delta like non-canonical Notch ligand 1; TMZ, trimetazidine; LPSF/GQ-02, a thiazolidinone derivative; SARM1, sterile alpha and armadillo motif-containing protein 1; Rg1, ginsenoside Rg1; QSHX, a kind of Chinese medicine extract; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; S100A11, S100 calcium binding protein A11; FcγRIIb, Fc-gamma receptor-IIb; n3-PUFAs, n3-polyunsaturated fatty acids; As1842856, a specific inhibitor of FOXO1; LncRNA SRA, long non-coding RNA steroid receptor RNA activator; LncRNA MEG3, long non-coding RNA maternally expressed 3.