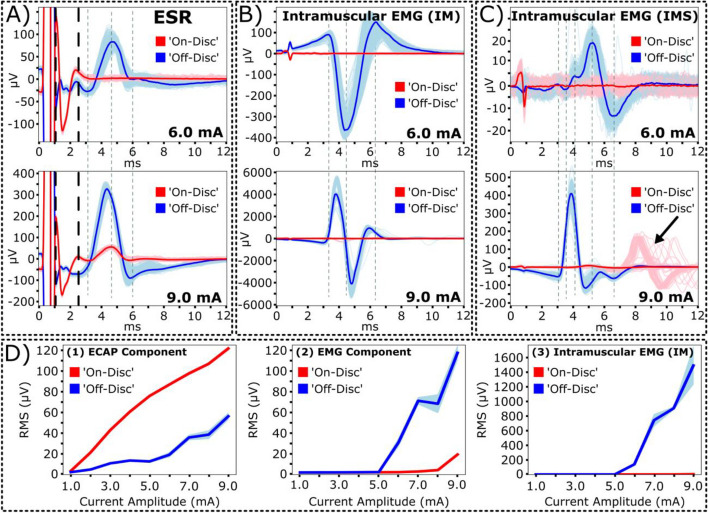
Fig. 5.
Evoked ESRs are responsive to the anatomical location of the stimulating cathode. Representative data from subject S3. Waveforms were represented as 300 individual recorded traces with an overlaid median trace. A Cathodic ‘off-disc’ stimulation resulted in observable EMG bleed-through for recorded ESRs compared to the ‘on-disc’ stimulation. B Intramuscular EMG recordings of the intercostal muscles via surgical placement of needle electrodes through the intercostal muscles (IM) and C through the skin (IMS) show preference for evoked muscle contraction when cathode was located ‘on-disc’. Cathodic ‘on-disc’ stimulation produced a delayed motor response at the maximum stimulation amplitude, 9.0 mA, for intramuscular EMG (IMS) recordings, as indicated by a black arrow (bottom). D Dose-response curves (calculated as root-mean-square, RMS) for collected ESRs, shown as (1) ECAP and (2) EMG components, and (3) intramuscular EMG (IM) recordings show a distinct relationship to cathode placement with respect to the intervertebral disc