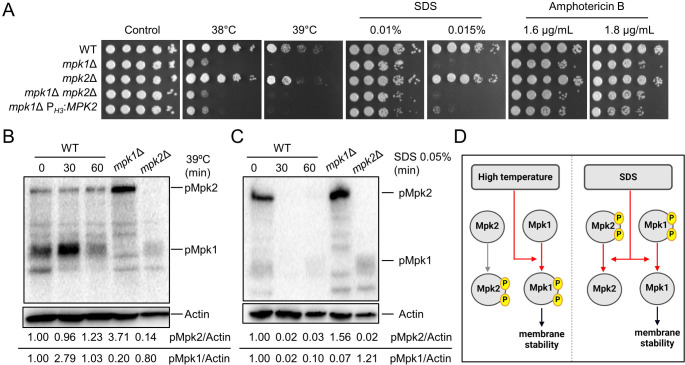
Fig 5.
Mpk1 and Mpk2 play distinct roles in maintaining cell membrane integrity. (A) Wild-type, mpk1Δ, mpk2Δ, mpk1Δ mpk2Δ, and mpk1Δ PH3:MPK2 strains were cultured overnight and then subjected to spot assays under various membrane stresses including high temperature, SDS, and amphotericin B. The photos were taken on day 3. (B and C) Wild-type, mpk1Δ, and mpk2Δ strains were cultured overnight and subcultured to an OD600 of 0.8 before being treated with high temperature at 39°C or 0.05% SDS. After the treatment, samples were harvested at 0, 30, and 60 min and frozen in liquid nitrogen before protein extraction. The extracted proteins were quantified, loaded in equal amounts, and subjected to western blot to assess the levels of phosphorylated Mpk1 and Mpk2. Additionally, after stripping the membrane, reprobing was conducted with an anti-actin antibody to quantify the total protein. (D) A schematic of the proposed Mpk1/Mpk2 regulatory mechanisms for maintaining cell membrane integrity in C. neoformans