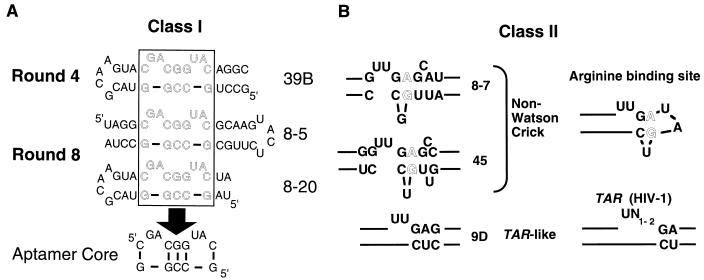
FIG. 3.
Sequence and structural motifs in anti-Rex aptamers. Aptamers were grouped into families based on comparisons between the sequences and predicted secondary structures of anti-Rex aptamers isolated from round 4 and round 8. (A) Class I aptamers. The similar sequences and stem-bulge structures characteristic of class I aptamers could be found in either orientation relative to the capping stem-loop structure. For example, aptamers 39B and 8-20 are in one orientation, while aptamer 8-5 is in the opposite orientation. A common set of nucleotides (boxed region) are found in the most populous, highest-affinity binding species. (B) Class II aptamers. The Class II aptamers contain a sequence and predicted structural motif that is similar to an arginine-binding motif previously observed in HIV-1 TAR elements and other RNA molecules. For example, aptamer 9D (left) contains a sequence and predicted structural motif similar to HIV-1 TAR (right). Similarly, aptamers 8-7 and 45 (left) contain non-Watson-Crick base pairs similar to arginine-binding motifs previously identified by in vitro selection (right) (49). Lines indicate nucleotides that extend outside of the highlighted domain.