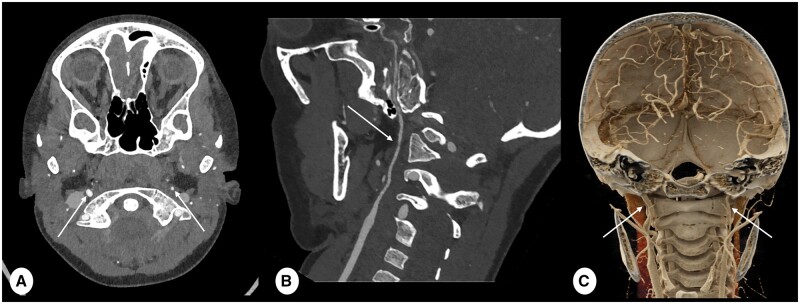
Figure 1.
CT angiography (CTA) scan of a 7-year-old male with a hypoplastic carotid artery. (A) an axial ultra-high resolution (UHR) CTA is captured with a slice thickness of 0.2 mm, employing kernel Hv56 and iterative reconstruction (IR) level 4 (Q4). This image distinctly illustrates the disparity in size between the left hypoplastic internal carotid artery (ICA) (indicated by the thin arrow) and the right ICA (indicated by the thick arrow). (B) It corresponds to the curved planar reformat (CPR) along the central line of the left hypoplastic ICA (arrow). Meanwhile, (C) offers a coronal volume rendering of (A), accentuating the identical difference in calibre between the left hypoplastic ICA (thin arrow) and the right ICA (thick arrow). Note that the implementation of UHR scanning in combination with a reconstruction technique optimized for vascular structures, greatly enhances the crisp definition of vessel contours, significantly simplifying the assessment of vascular structures and enabling high quality multiplane reconstructions.