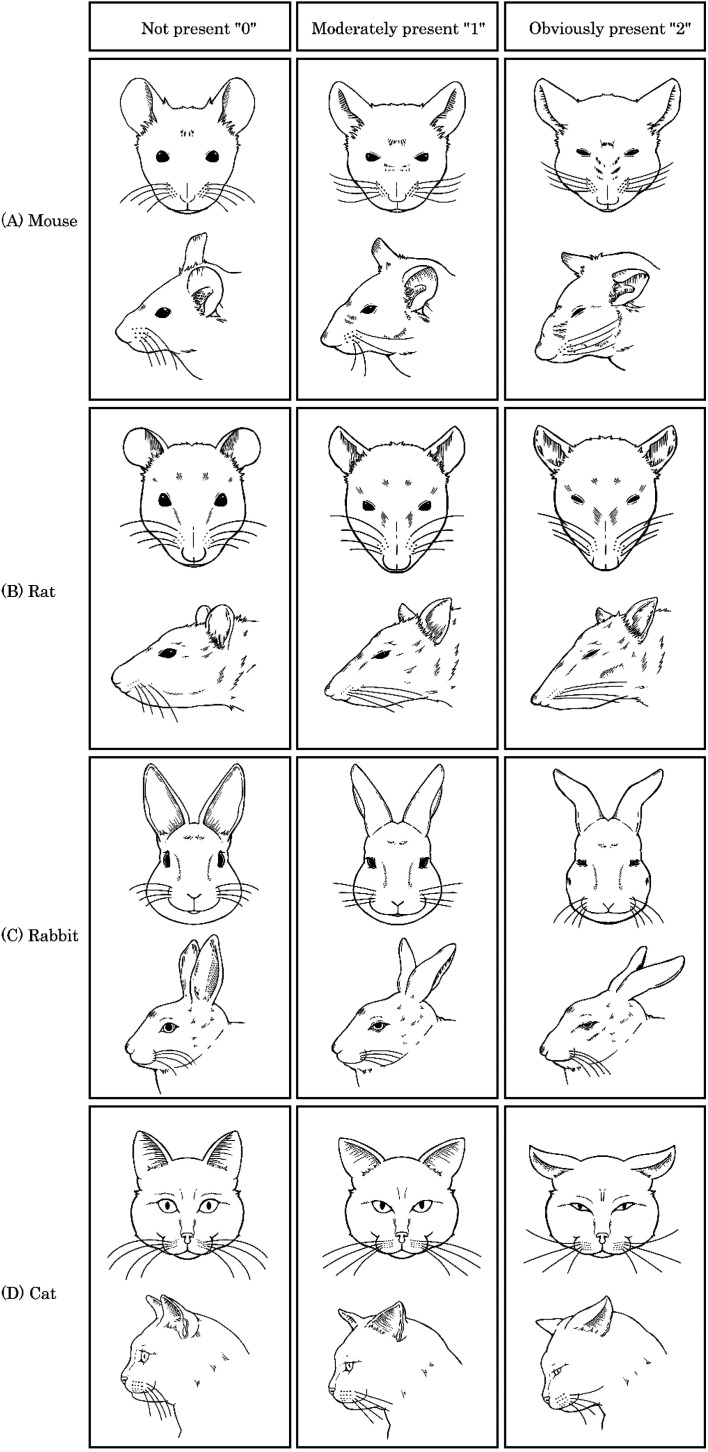
Fig. 1.
Differences in facial expressions due to pain in various animals. Differences in facial expressions due to pain in various animals were categorized into three levels of pain intensity: none (0), moderate (1), and clearly present (2). Commonly observed behavior in animals when experiencing pain includes squinting of the eyes. (A) In mice, the nose and cheeks bulge, the ears do not face forward, and there is an increased gap between them. The whiskers either curve backward along the cheeks or stand up forward. (B) In rats, the nose and cheeks become flatter, the ears take on a pointed shape, and the gap widens. The whiskers become stiff and angle along the face. (C) In rabbits, the cheeks become flatter, the nostrils change from a “U” to a “V” shape, the ears fold inwards to a cylindrical shape, and the whiskers stand away from the cheeks and point downwards. (D) In cats, the snout widens into a horizontal elliptical shape, the ears become pointed, the whiskers remain straight and forward, and the head tilts below or in front of the shoulder line.