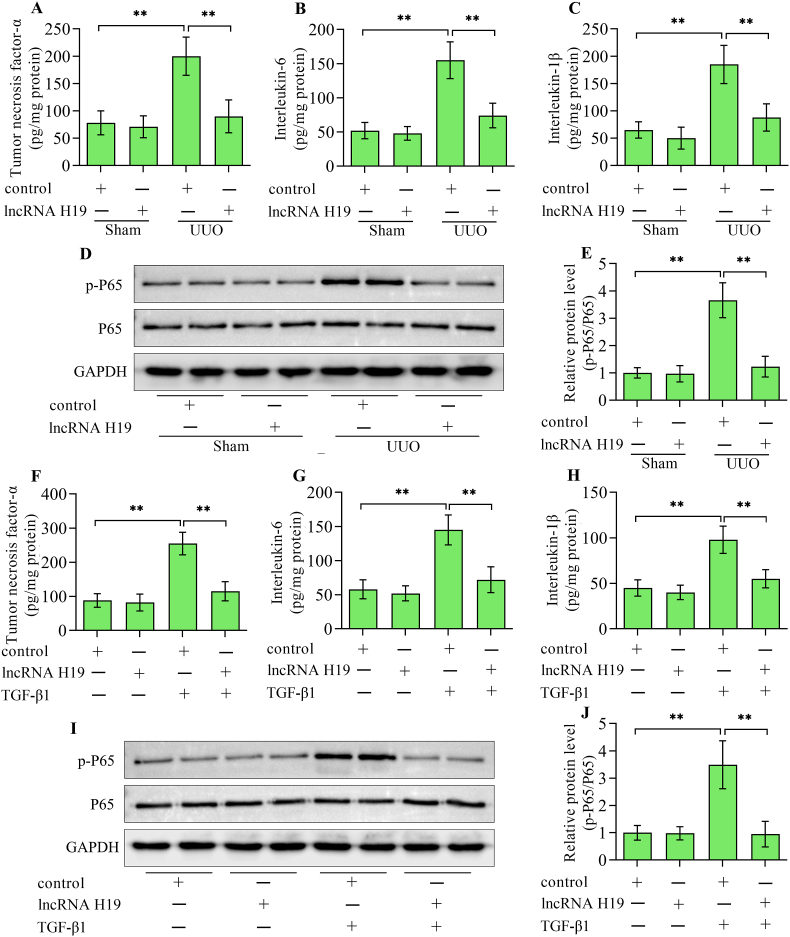
Fig. 3.
Effect of lncRNA H19 overexpression on inflammatory response. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detection of (A) tumor necrosis factor-α, (B) interleukin-6 and (C) interleukin-1β in kidneys from sham and UUO mice infected with adenoviruses expressing lncRNA H19 or control adenoviruses (n = 3). (D) Western blotting detection and (E) quantification of nuclear factor-κB P65 in kidneys from sham and UUO mice infected with adenoviruses expressing lncRNA H19 or control adenoviruses (n = 3). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detection of (F) tumor necrosis factor-α, (G) interleukin-6 and (H) interleukin-1β in HK-2 cells infected with adenoviruses expressing lncRNA H19 or control adenoviruses following TGF-β1 stimulation (n = 3). (I) Western blotting detection and (J) quantification of nuclear factor-κB P65 in HK-2 cells infected with adenoviruses expressing lncRNA H19 or control adenoviruses following TGF-β1 stimulation (n = 3). Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation, **p < 0.01. UUO, unilateral ureteral obstruction; P65, nuclear factor-κB P65; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1.