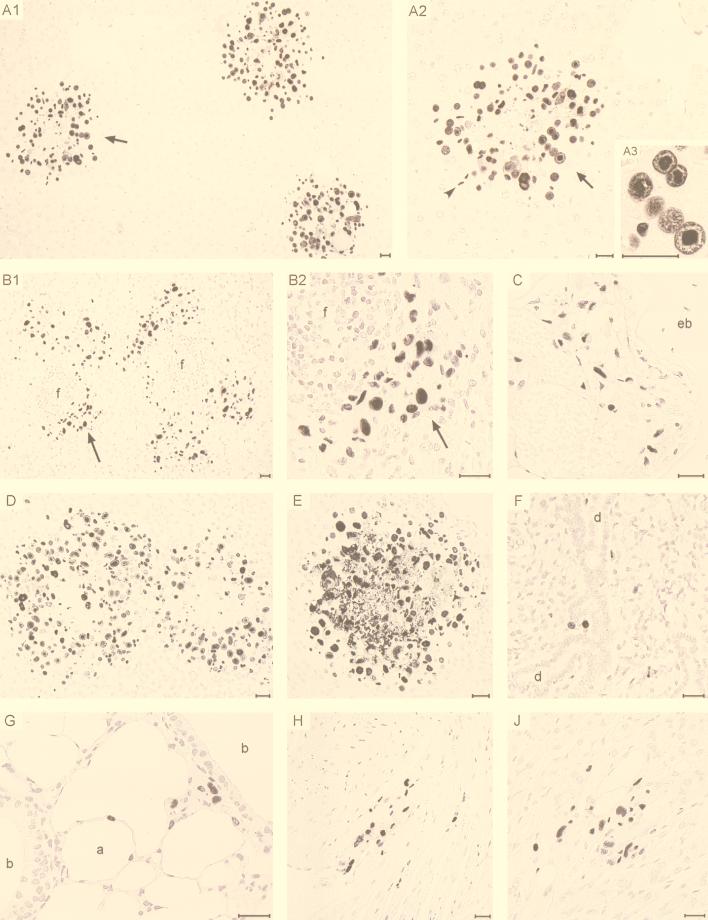
FIG. 7.
Tissue distribution and cell-type tropism of MIEPE swap mutant mCMVhMIEPE. Immunohistological analysis specific for the IE1 protein was performed on day 9 after infection with mCMVhMIEPE. (A1 to A3) Infection of liver parenchyma. A1, overview demonstrating advanced foci of infection; A2, enlargement of the portion of A1 indicated by the arrow, demonstrating the infection’s plaque-like character with a necrotic center. Infected cells were mostly hepatocytes, but endothelial cells (arrowhead) and a few Kupffer cells (not visible) were also present. A3, detail showing condensation of the IE1 protein in the intranuclear inclusion body of infected hepatocytes. (B1 to B2) Infection of perifollicular stromal cells in the spleen. B1, overview; B2, detail of the portion of B1 indicated by the arrow. f, remnants of follicles. (C) Infection of bone marrow stromal cells in the epiphysial region of a femur. eb, epiphysial bone. (D) Infection of adrenal medulla. Shown is a pair of huge, plaque-like foci in the medullary parenchyma. (E) Infection of adrenal cortex. Shown is an advanced focus extending from the zona glomerulosa deeply into the zona fasciculata. (F) Few infected glandular epithelial cells were present in the acini of the submandibular gland. d, duct system of salivary gland. (G) Infection of the lungs. Visible are infected cells in the alveolar septa and in the peribronchiolar connective tissue. Other sections show also infected capillary endothelial cells. a, alveolus; b, bronchioli. (H) Infection of cardiac muscle cells. (J) Infection of gastric mucosa. Counterstaining was performed with hematoxylin. Bars represent 25 μm.