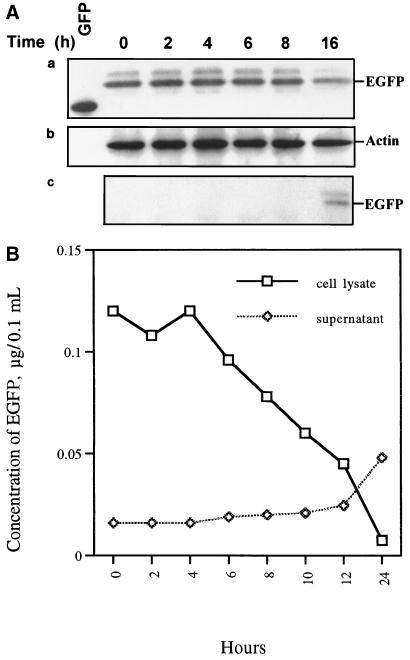
FIG. 4.
Patterns of EGFP release by CHSE-214-EGFP cells infected with IPNV. (A, parts a to c) Detection of EGFP release pattern due to IPNV infection by Western blotting. CHSE-214-EGFP cells were infected with IPNV (MOI of 1). Samples were electrophoresed on an SDS-polyacrylamide gel and electroblotted to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane either contained a rabbit polyclonal antiserum directed against EGFP (part a and c) or was stripped and reprobed with a mouse IgG monoclonal antibody directed against actin (part b). The chemiluminescent signal was imaged on Kodak XAR-5 film using a 3-min (part a), 1.5-min (part b), or 30-min (part c) exposure. (a) Lanes: 1, 0.45 μg of wild-type GFP; 2 to 7, 30 μg of virus-infected CHSE-214 cell lysate at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 16 h p.i., respectively. (b) The nitrocellulose membrane in part a was stripped and reprobed with anti-actin monoclonal IgG. (c) A 30-μg sample of supernatant protein of IPNV-infected CHSE-214-EGFP cells at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h p.i., respectively. (B) Rate of EGFP release by CHSE-214-EGFP cells infected with IPNV. Cellular and culture medium EGFP samples were prepared for assay in EGFP release experiments. About 105 cells per ml were seeded on a 60-mm petri dish and incubated for more than 20 h. Cells that received virus at an MOI of 1 were incubated for 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h p.i. At the end of each incubation time, the IPNV-infected CHSE-214 cells and culture medium were collected to determine the concentration of retained EGFP. Both 5 μg of lysed virus-infected cells per sample and 30 μg of supernatant medium per sample were counted by a Fluorolite 1000. The EGFP concentrations of the lysed cells and supernatant were evaluated by using a Fluorolite 1000 to compare them with standard GFP protein and dividing by 35 (6).