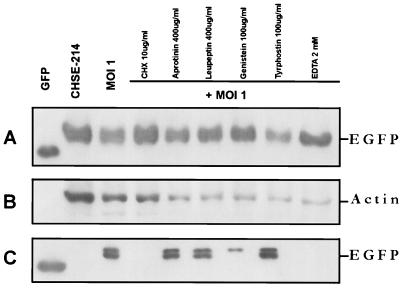
FIG. 6.
Western blot assay of the effect of chemical inhibitors on EGFP release. Protein synthesis inhibitors, serine proteinase inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and a cation chelator were added to CHSE-214-EGFP cells before infection with IPNV (MOI of 1). After infection, the cells were incubated for 16 h. Samples were electrophoresed on an SDS–12% polyacrylamide gel and electroblotted to a nitrocellulose membrane. Antigen-specific signals were detected with either rabbit anti-GFP serum (A and C) or a mouse IgG monoclonal antibody directed against actin (B). The chemiluminescent signal was imaged on Kodak XAR-5 film by using a 5-min (A), a 1-min (B), or a 30-min (C) exposure. (A) Lanes: 1, 0.2 μg of recombinant wild-type GFP as a positive control; 2, normal CHSE-214-EGFP cell lysate; 3, 30 μg of cell lysate protein corresponding to treatment with CHX (100 μg/ml), aprotinin (400 μg/ml), leupeptin (400 μg/ml), genistein (100 μg/ml), tyrphostin (100 μg/ml), and EDTA (2 mM) and then virus infected for 16 h, respectively. (B) The nitrocellulose membrane from panel A was stripped and reprobed with an actin antibody. (C) Lanes: 1, 100 ng of wild-type GFP; 2, 30 μg of supernatant medium protein from IPNV-infected cells at 16 h p.i. 4 to 9, 30 μg of supernatant medium protein corresponding to treatment with CHX (100 μg/ml), aprotinin (400 μg/ml), leupeptin (400 μg/ml), genistein (100 μg/ml), tyrphostin (100 μg/ml), and EDTA (2 mM) before virus infection and at 16 h p.i., respectively.