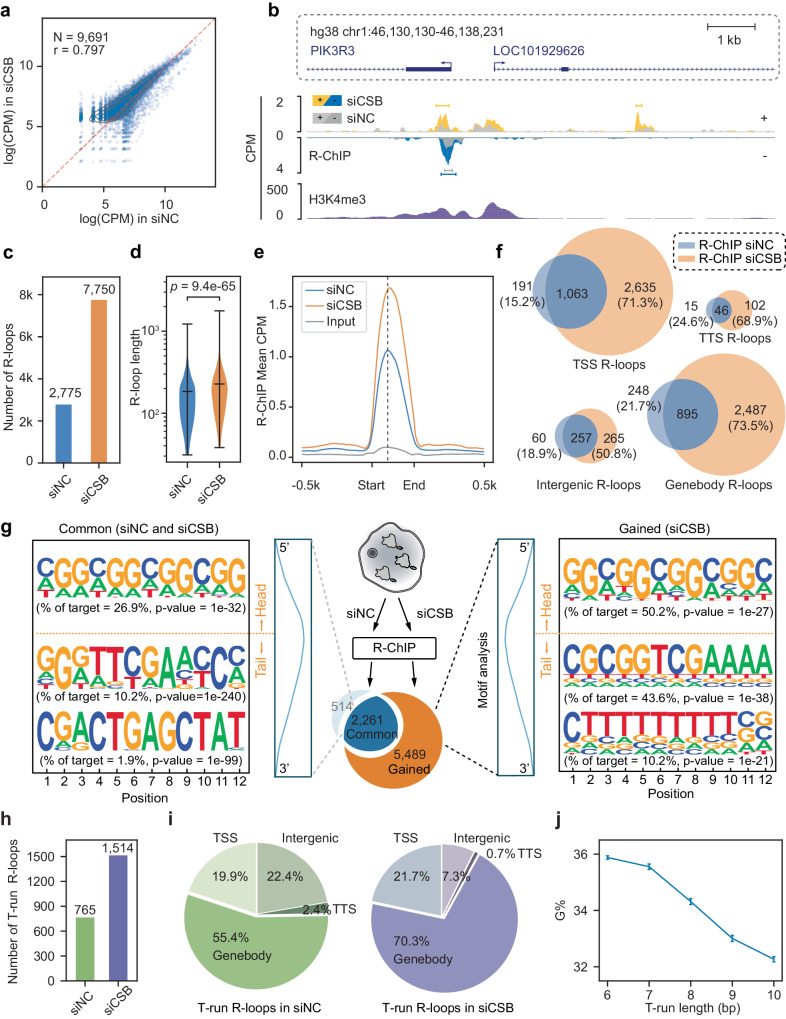
Fig. 1. Depletion of CSB enhances R-loop formation.
a Scatter plot of R-ChIP, showing R-loop signals in mock-treated (siNC; X-axis) versus CSB-depleted HEK293 cells (siCSB; Y-axis). Each dot represents an R-loop peak region. The scale for both X-axis and Y-axis is log(CPM + 1); CPM: count per million. b Genome browser tracks showing a region containing R-loop signals from R-ChIP and public H3K4me3 signals on both the up (+) strand (gray and yellow) and lower (−) strand (gray and blue) in siNC-treated (gray) and siCSB-treated (yellow or blue) HEK293 cells. Gene annotations are shown on top of the tracks. c R-loop number profile under siNC and siCSB treatment conditions. d R-loop length distribution under siNC and siCSB treatment conditions. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test. e Metaplot of R-loop signals in siNC (blue) and siCSB (orange) treated HEK293 cells. Signals are centered on the R-loop summit on ±0.5 kb surrounding regions. f Venn diagrams of R-loops at TSSs (transcription start sites), Genebodies, TTSs transcription termination sites, and Intergenic regions. g Motifs enriched on R-loops. Motif enrichment in the head half and tail half was separately analyzed. Along with each enriched motif is the frequency and associated p-value. Shared and siCSB-induced R-loops are displayed on the left and right, respectively. h, i The number of T-run associated R-loops detected in siNC and siCSB-treated HEK293 cells (h) and the distribution of their genomic locations (i). j G percentage in relationship with the length of T-run on individual R-loops. The plot shows the average G percentage in non-template DNA vs the length of T-run in common T-run-associated R-loops. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n = 172, 61, 59, 52, and 69 common T-run-associated R-loops, from left to right).