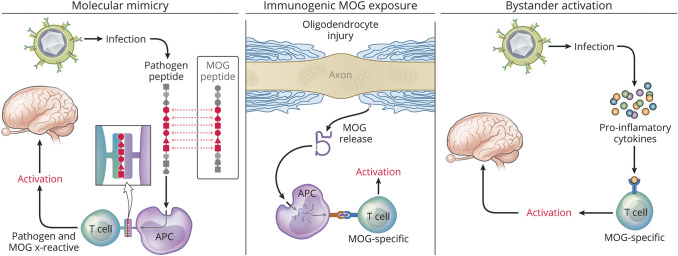
Figure 4. Potential Triggers of MOG Autoimmunity.
Several possible mechanisms may promote MOG CNS autoimmune disease. MOG autoimmunity could be triggered by molecular mimicry (left panel), a process that can occur when antigenic determinants of pathogens cross-react with self-antigens. Immunogenic MOG exposure (middle panel), either from CNS damage secondary from another disease,55 or ectopic MOG expression54 could promote activation of MOG-specific immune cells. The normal immune repertoire contains MOG-reactive T cells. Thus, bystander activation (right panel) of preexisting MOG-specific T cells by proinflammatory cytokines from an unrelated stimulus (e.g., systemic infection) could theoretically lead to proinflammatory polarization and expansion of MOG-specific T cells. Copyright Xavier Studio, reprinted with permission.