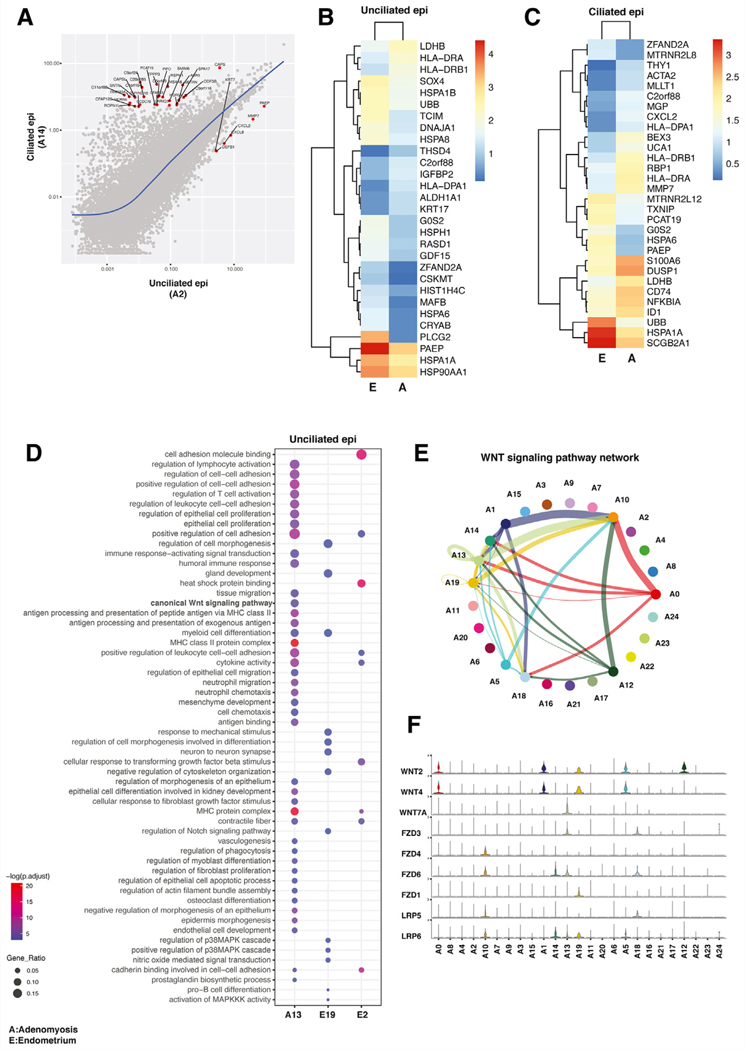
FIGURE 4.
Analysis of epithelial cell profiles in adenomyosis and endometrium. (A) Molecular characterization of epithelial cell types in adenomyosis. Scatter plot showing average log fold change in gene expression between ciliated epithelial cells and unciliated epithelial cells in adenomyotic tissue. Expression of only several select genes, such as PAEP, defined the specific transcriptional profile of unciliated epithelial cells. (B) Heatmap of highly expressed genes in unciliated epithelial cells in adenomyosis (A) versus endometrium (E). Expression of PAEP, a well-defined progesterone-responsive differentiation marker, is significantly higher in endometrial unciliated cells. (C) Heatmap of highly expressed genes in ciliated epithelial cells in adenomyosis (A) versus endometrium (E). Secretoglobin 2A1 (SCGB2A1) is prominently expressed in ciliated endometrial cells. (D) Over-representation analysis comparing the single unciliated epithelial cell cluster in adenomyosis (A13) compared with the 2 unciliated epithelial clusters in endometrium (E19 and E2). The canonical WNT pathway was uniquely activated in the adenomyotic ciliated epithelial cell cluster. (E) Inferred communication network of the entire WNT signaling pathway in adenomyosis. The general signaling direction is such that WNT ligands originate primarily from the fibroblast-like cells (A0, A1, A5 and A12), whereas the primary WNT-responsive cell types are the epithelial and endothelial cells. A13 unciliated epithelial cell cluster is unique in that it shows an autocrine signaling pattern; moreover, A13 epithelial cells also send signals to ciliated epithelial (A18) and endothelial (A10) cells. (F) Expression of WNT signaling pathway genes in each cell cluster in adenomyosis. The general pattern of expression is such that the WNT ligands are highly expressed in fibroblast-like cells, whereas their receptors or coreceptors are prominently expressed in epithelial and endothelial cells.