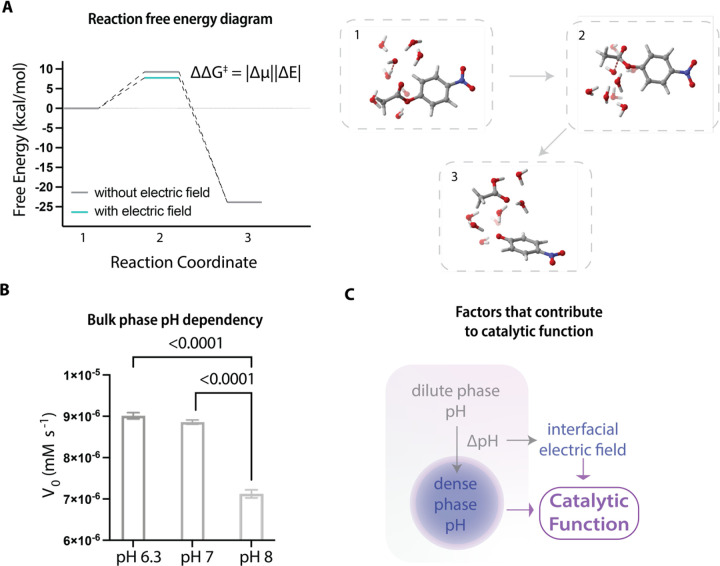
Figure 2. Evaluation of the role of interfacial electric fields on driving hydrolysis reactions.
A, The reaction free energy diagram calculated based on DFT shows the effect of external electric fields on lowering the free energy barrier of the transition state of pNPA hydrolysis. The right panel shows the entire hydrolysis reaction pathway calculated with an explicit first solvation shell (with 7 H2O molecules) combined with a conductor-like polarizable continuum model (CPCM).
B, The bulk phase pH dependency of catalytic behavior of RLPWT condensates. RLPWT condensates under different bulk phase pH conditions can generate different interphase pH gradients cross the phases, while maintaining a similar dense phase alkaline pH. This gives rise to distinct initial rates for pNPA catalysis.
C, The dominating factors contributing to the catalytic functions of condensates are the dense phase chemical environment and the interfacial electric field.