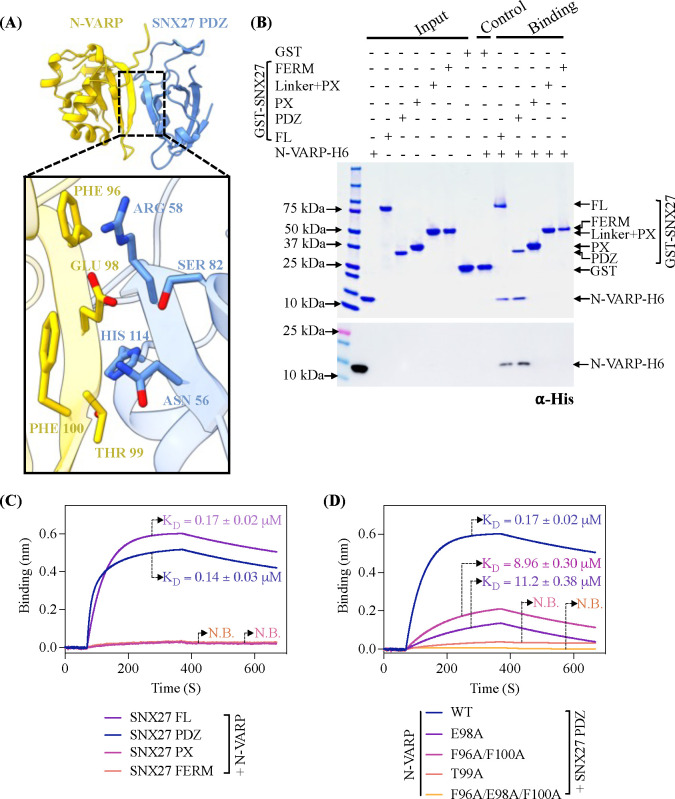
Figure 2. The VARP N-terminal domain directly binds SNX27 PDZ domain.
(A) Ribbon diagrams of AlphaFold2.3 Multimer complex model between N-VARP (gold) and SNX27 PDZ (sky blue). The boxed inset shows interacting side chain residues on N-VARP (gold sticks) and SNX27 PDZ (blue sticks). (B) Pulldown experiments with purified GST-SNX27 fusion proteins. SNX27 full-length (FL), PDZ, PX, or FERM domains were used as bait with N-VARP-H6 as prey. A representative SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie blue is shown in top panel with ⍺-His Western blot shown in bottom panel. (C) Biophysical data using BLI Octet system reveal a low micromolar affinity between SNX27 and N-VARP. Biotinylated N-VARP was loaded onto Streptavidin biosensor for measurements with SNX27 purified proteins. (D) Hydrophobic residues on VARP drive binding to SNX27. Biotinylated N-VARP mutants (E98A; T99A; F96A/F100A; F96A/E98A/F100A) were loaded onto Streptavidin biosensor for measurements with the SNX27 PDZ domain. Fitted data were plotted in GraphPad Prism, and binding kinetics were calculated using the Octet R8 analysis software package.