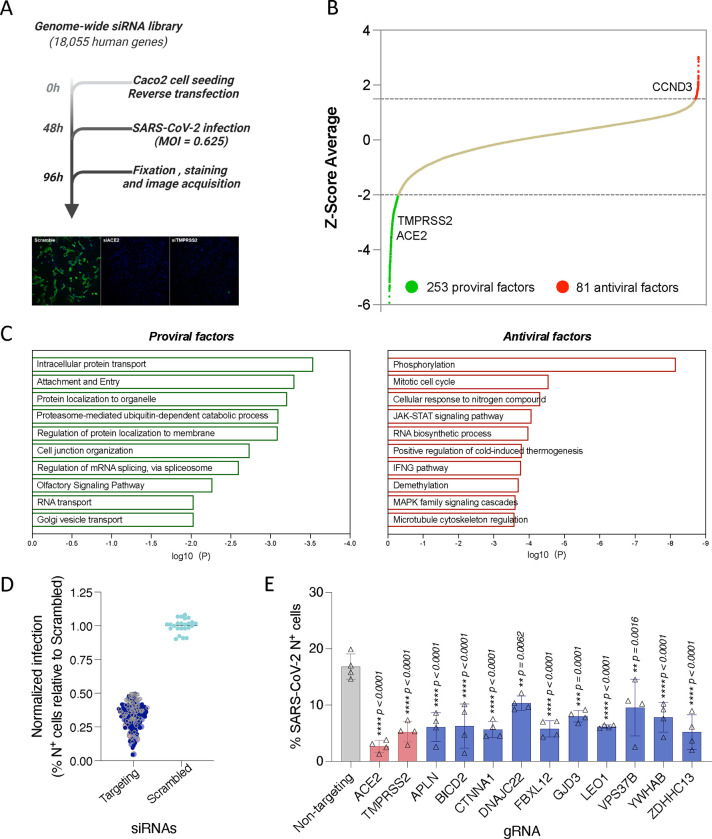
Figure 1 – Genome-wide siRNA screen identifies host factors involved in SARS-CoV-2 replication.
(A) Schematic representation of the genome-wide screen to identify human host factors that affect SARS-CoV-2 replication. (B) Ranked SARS-CoV-2 infectivity Z-scores from the genome-wide siRNA screen. Dashed lines illustrate cut-offs for hit calling strategy: Z-score ≤ −2 indicates proviral factors (green), Z-score ≥ 1.5 indicates antiviral factors (red). Controls are shown (e.g., siACE2, positive). (C) Functional enrichment analysis of identified proviral (left-green) and antiviral (right-red) host factors. (D) Deconvolution plot showing proviral host factors validated with one siRNA (grey), two siRNAs (dark blue), three siRNAs (light blue) and four siRNAs (pink). (E) Calu-3 cells treated with indicated gRNAs were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI = 0.75) for 48 h prior to immunostaining for viral N protein. Shown is quantification of the normalized infection (% of SARS-CoV-2 N+ cells) relative to parental cells. Data show mean ± SD from one representative experiment in quadruplicate (n=4) of two independent experiments. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test.