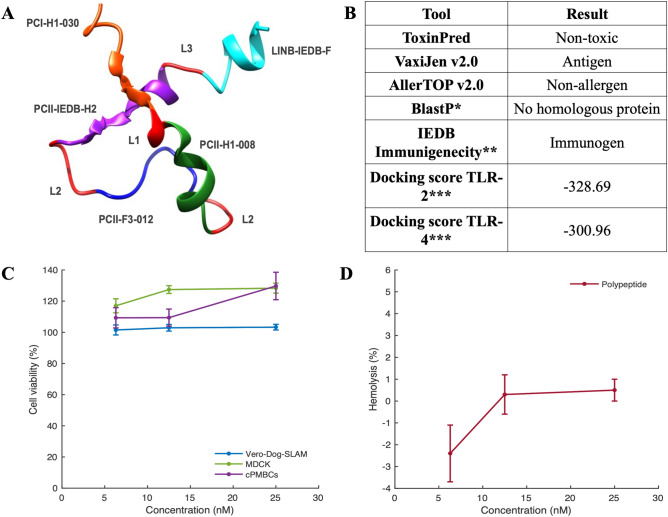
Figure 6.
Multiepitope polypeptide characteristics and in silico and in vitro safety validation. (A) Structural model of the multiepitope polypeptide obtained with I-TASSER. (B) In silico safety validation data for the polypeptide. (C) Evaluation of the viability of Vero-Dog-SLAM, MDCK and cPBMC cells after polypeptide treatment through the MTT assay. Cells were treated with twofold serial dilutions of polypeptide from 6.125 to 25 nM for 48 h. Cells without polypeptide were used as a viability negative control, and cells treated with 0.5% Triton X-100® served as a cytotoxicity positive control. (D) Hemolytic potential of the polypeptide in canine RBCs. PBS was used as a negative hemolytic control, and 0.1% Triton X-100® was used as a positive hemolytic control. Two independent experiments with 4 replicates (n = 8) were carried out, and nontreated cells were used as negative controls. The means and coefficients of variation are shown in the graph. *Evaluated with the Canis lupus familiaris proteome as the dataset. **Score of 0.57349, classified as a probable antigen MCH-I. ***Docking score obtained with the HPEPDOCK tool.