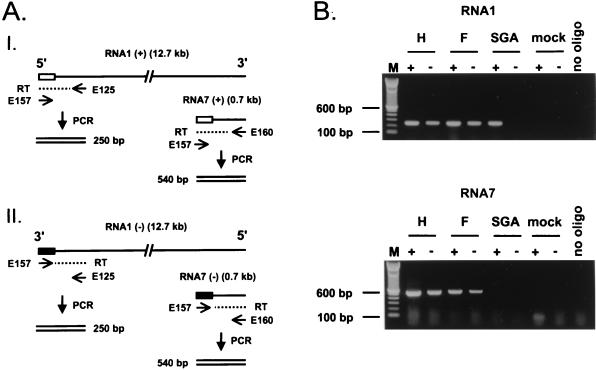
FIG. 4.
(A) RT-PCR strategy for the detection of positive-stranded (I) and negative-stranded (II) genomic RNA and sg RNA7. Leader and antileader sequence are indicated with white and black boxes, respectively. Oligonucleotides E125 and E160 are directed against the body sequences of RNA1 and sg RNA7, respectively, and are used for priming cDNA synthesis (dashed line) on the positive strands of RNA1 and RNA7. Oligonucleotide E157 is directed against the antileader sequence (black box) and is used for cDNA synthesis on the negative strand. For the PCR, oligonucleotides E157 and E125 are used to amplify regions specific for positive- and negative-stranded RNA1. Oligonucleotides E157 and E160 are used for the PCR specific for positive- and negative-stranded sg RNA7. (B) RT-PCR analysis for the positive and negative strands of RNA1 (top panel) and positive and negative strands of sg RNA7 (bottom panel). The RNA was isolated from cells transfected with EAV030H (lanes H), EAV030F (lanes F), or EAV030SGA (lanes SGA) or from mock-transfected cells. The plus and minus signs indicate specificity of the RT-PCR for positive and negative strands, respectively.