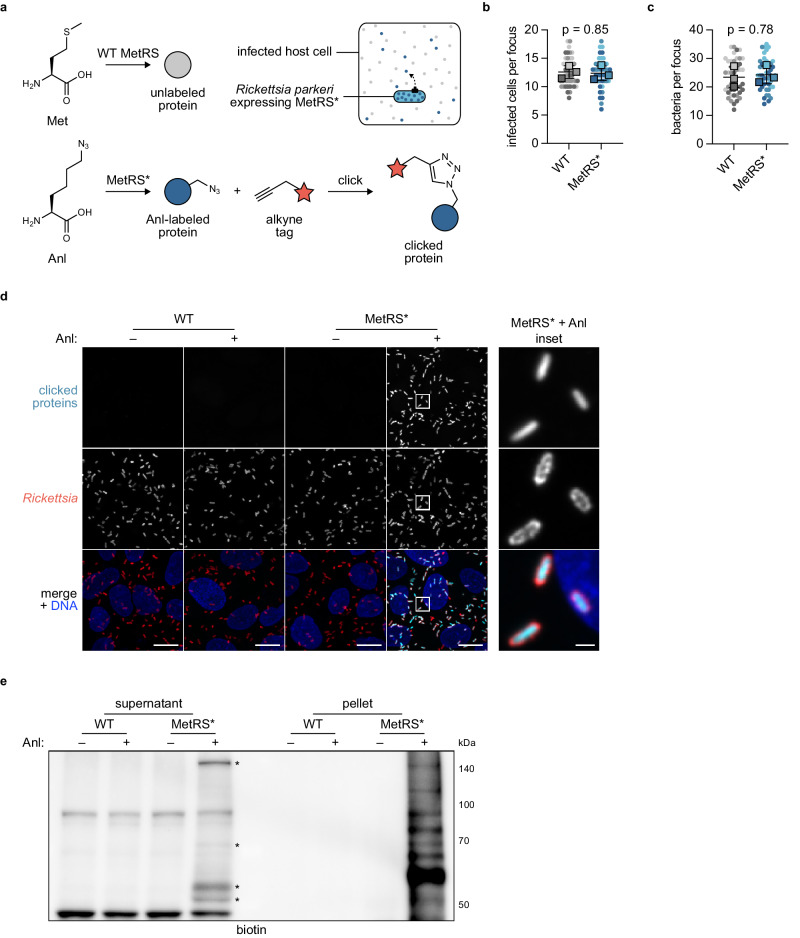
Fig. 1. BONCAT permits selective labeling of rickettsial proteins.
a Schematic of BONCAT approach. Rickettsia parkeri expressing a mutant methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MetRS*) incorporates the Met analog azidonorleucine (Anl) into nascent proteins, some of which are secreted into the host cell during infection. Anl-labeled proteins (blue circle), but not unlabeled proteins (gray circle), are tagged (red star) by click chemistry. Wild-type (WT) MetRS cannot accommodate Anl. b Infected cells and c bacteria per focus during infection of A549 cells by WT or MetRS* R. parkeri. The means from n = 3 independent experiments (squares) are superimposed over the raw data (circles) and were used to calculate the means ± SD and p-values (unpaired two-tailed t-test, t = 0.206 and 0.297, df = 4). Data are shaded by replicate experiments. d Images of WT and MetRS* R. parkeri treated with (+) or without (–) Anl during infection of A549 cells (Hoechst, blue). Bacteria were permeabilized and stained (red), and Anl-labeled proteins were detected by tagging with an alkyne-functionalized fluorescent dye (cyan). Scale bar, 10 μm (inset, 1 μm). e Western blot for biotin in lysates harvested from A549 cells infected with WT or MetRS* R. parkeri with (+) or without (–) Anl treatment. Infected host cells were selectively lysed to separate supernatants containing the infected host cytoplasm from pellets containing intact bacteria. Anl-labeled proteins were detected by tagging with alkyne-functionalized biotin. Asterisks indicate putative secreted effector bands. Results for (d) and (e) are representative of at least three independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.