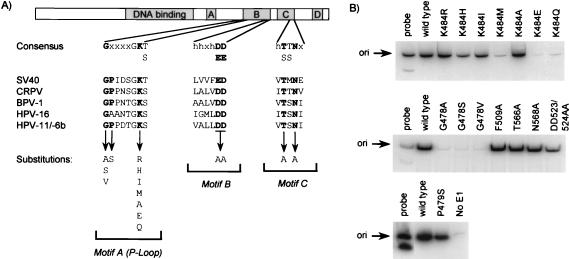
FIG. 4.
Effects of substitutions in the ATP-binding domain of E1 on the E2-dependent binding of E1 to the origin. (A) Diagram of the E1 helicase. The shaded boxes indicate the positions of conserved regions A, B, C, and D and of the DNA-binding domain. The locations of conserved motifs A, B, and C that are present in members of superfamily 3 of the NTP-binding proteins (20) are indicated. The consensus amino acid sequence of each motif is indicated, as well as a sequence alignment between SV40 T antigen and the E1 proteins of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus, BPV-1, HPV-16, HPV-11, and HPV-6b. Residues that were mutated are shown in boldface. (B) E2-dependent binding of mutant E1 proteins to the origin (ori). DNA-protein complexes were assembled with E2 and the indicated E1 protein made by in vitro translation. The immunoprecipitation of complexes was performed with the rabbit K72 polyclonal antibody. Detection of bound DNA was done as described in the legend to Fig. 2A.