FIGURE 1.
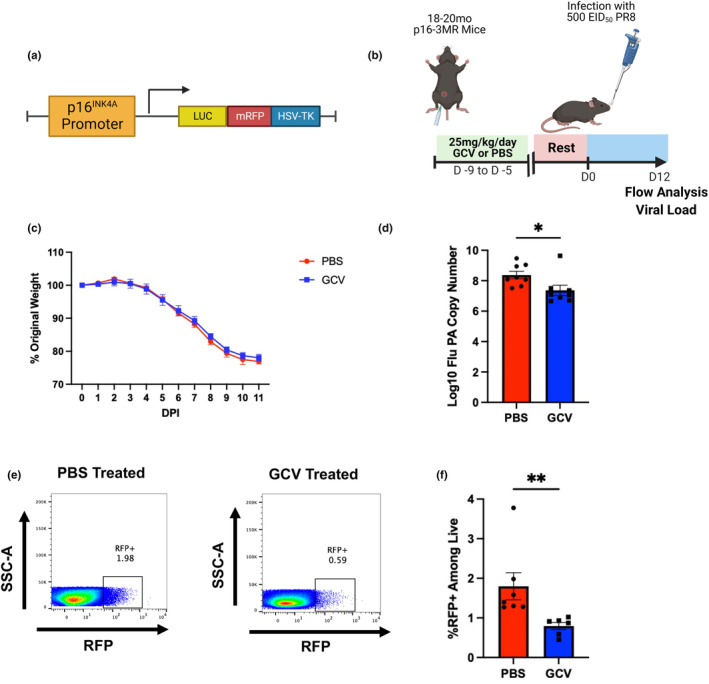
Targeting p16‐Expressing Cells is Effective in Potentiating the Primary Aged Antiviral Immune Response. The p16‐trimodality reporter (p16‐3MR) model expresses a fusion protein with three domains under the control of the p16INK4A promoter: one expressing luciferase, another expressing mRFP, and another expressing the herpesvirus thymidine kinase (a). To study the effects of p16‐expressing cells on the aged immune response to influenza, we treated 18‐20mo p16‐3MR mice with 25 mg/kg/day ganciclovir (GCV) or PBS for 5 days. Following a 5 days rest period, we infected mice with sublethal dose of influenza (b). Percent of original weight lost was tracked throughout the course of infection with PR8 flu (c). At 12 days post infection (DPI) with PR8 flu, one cohort of mice was used to quantify viral load in the lungs via RT‐qPCR (d). RFP expression out of total live cells was quantified up to 30 DPI with x31 flu to confirm efficacy of GCV treatment (e,f). Data are presented as mean +/− standard error of the mean (SEM) and each symbol represents a single animal. Mann–Whitney U‐test was utilized for D and F, with a significance level of *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. N = 6–8 per group (for experiments shown in B‐D, 3 males in GCV group and 4 males in PBS group. For experiments shown in E and F, 4 males in GCV group and 4 males in PBS group).
