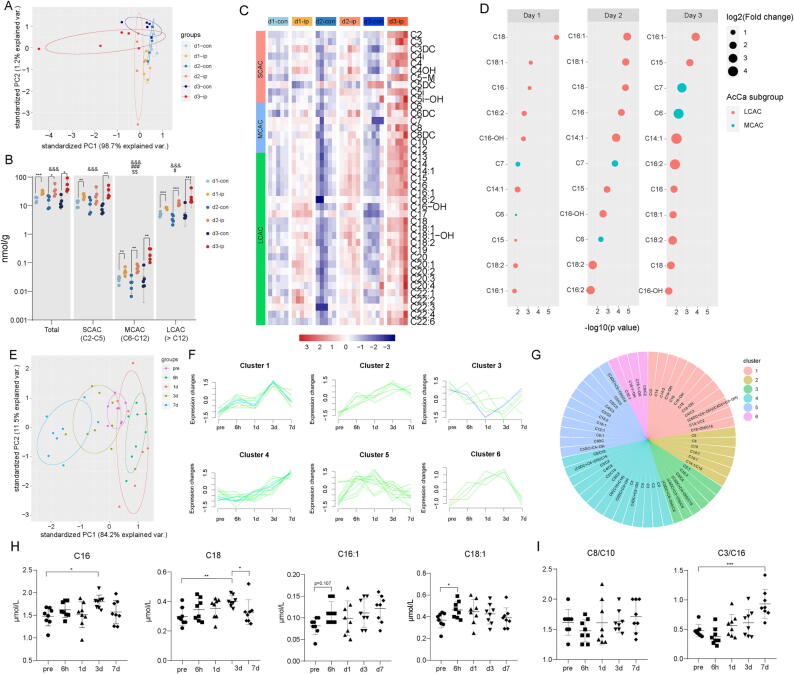
Fig. 2.
Acylcarnitine species accumulate markedly in the ischemic penumbra and peripheral blood in tMCAO mice. (A) PCA plot depicting separation of the ischemic penumbra (d1-ip, d2-ip, d3-ip) and corresponding contralateral area (d1-con, d2-con, d3-con) utilizing the first two components of the PCA model. (B) Concentration of total AcCa, SCAC, MCAC and LCAC in the ischemic penumbra and corresponding contralateral area among 3 days as measured by UHPLC-MS/MS. Data are presented as median ± max/min (N = 5 each group). Significant tMCAO effects (two-way ANOVA): &&&p < 0.001. Significant time effects (two-way ANOVA): #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. Significant tMCAO-time interaction effects: $p < 0.05, $$p < 0.01, $$$p < 0.001. Significant tMCAO effects within each day (unpaired, two-tailed t test): *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (C) Heatmap displaying the abundance of the 42 AcCa species in ischemic penumbra and corresponding contralateral area among 3 days. N = 5 each group. (D) Significantly accumulated AcCa species in the ischemic penumbra compared with corresponding contralateral area (p < 0.05 and FC > 1.5 within each day). Size of the circles indicates fold changes and colour of the circles indicates subgroups of AcCa. (E) PCA plot depicting separation of time-course lipidomic data from DBS samples of tMCAO mice 1 h before tMCAO as well as 6 h, 1 d, 3 d and 7 d after tMCAO. (F-G) Fuzzy c-means clustering identified 6 distinct temporal patterns of AcCa expression and AcCa species in each cluster were displayed. (H) Concentration of AcCa(C16), AcCa(C16:1), AcCa(C18), and AcCa(C18:1). Data are presented as mean ± SD (N = 8 each group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, repeated measures one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test for AcCa(C16) and AcCa(18:1) and Friedman’s test for AcCa(C16:1) and AcCa(C18). (I) Relative level of AcCa(C8/C10) and AcCa(C3/C16). ***p < 0.01, repeated measures one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test.