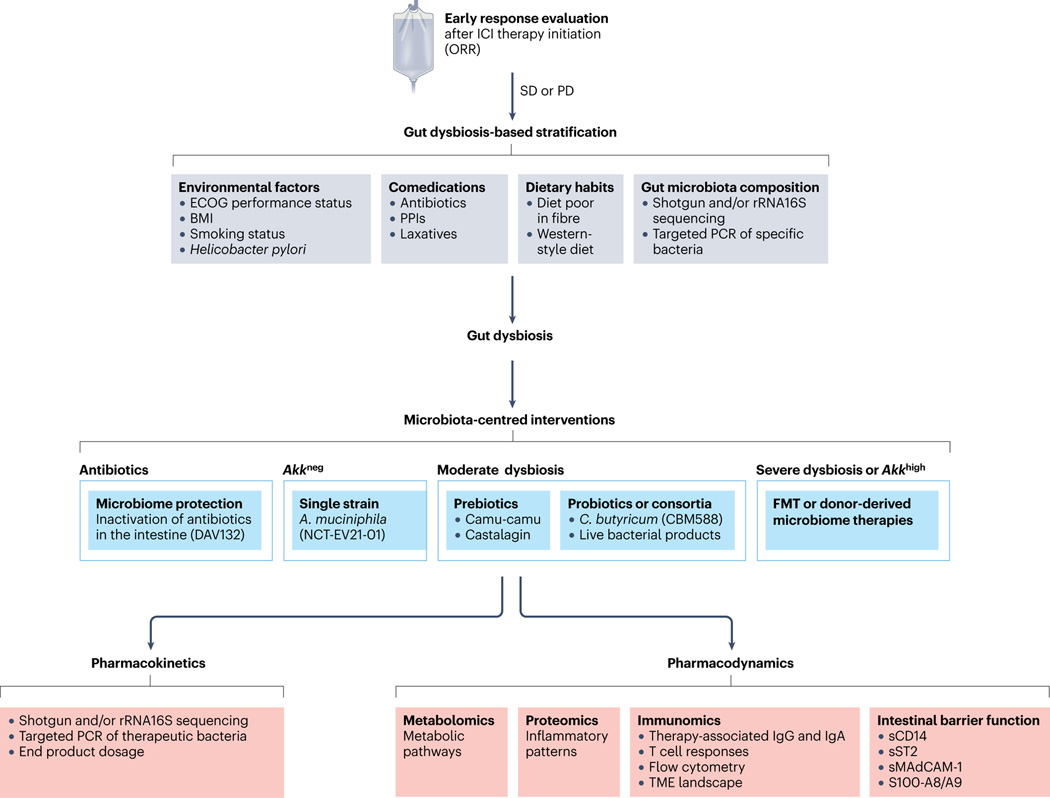
Fig. 6 |. Proposed pathway to define GOMS-based clinical guidelines.
Summary of the proposed clinical management of patients with cancer who could receive an approved immune-checkpoint inhibitor considering gut microbiota composition. Faecal samples from patients with a history of antibiotic treatment (any kind except vancomycin) taken between 60 days before and 42 days after the first administration of anti-PD-1 antibodies (alone or combined with anti-CTLA4 antibodies) or comedications known to alter microbiota composition (such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or laxatives) should be investigated using shotgun metagenomic sequencing or targeted PCR at diagnosis to monitor taxonomic composition. Depending on the relative abundances of Akkermansia spp. as well as other family members or genera or species (listed as harmful or beneficial in Gut OncoMicrobiome Signatures (GOMS)) (Figs. 3 and 4), different putative scenarios are described with their respective clinical management as for a potential microbiota-centred intervention to compensate for intestinal dysbiosis. The overabundance of Akkermansia spp. (SGB9226, SGB9228 or others) is defined as a relative abundance of >4.8% among all species using MetaphLAN or MetaO-MineR algorithms (defined as Akkhigh, as opposed to Akkneg). Several trials are evaluating interventions involving antibiotics (NCT02176005, NCT02917200), prebiotics (NCT05303493), Clostridium butyricum (NCT05122546, NCT03829111), live bacterial products (NCT03637803, NCT03775850, NCT04208958) and donor-derived therapies (NCT04116775, NCT05273255, NCT04758507, NCT05251389, NCT04577729, NCT04988841, NCT04975217, NCT05286294, NCT04924374, NCT04729322, NCT04264975, NCT04130763, NCT04521075, NCT04951583, NCT05502913, NCT03686202, NCT03817125). The pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of microbiota-centred interventions should be assessed to monitor their effects on the host metabolic, immunological or haematological functions or inflammatory tonus, and the gut microbiota composition or deviation from baseline. FMT, faecal microbiota transplantation; ICI, immune-checkpoint inhibitor; ORR, objective response rate; PD, progressive disease; sCD14, soluble CD14; SD, stable disease; sMAdCAM-1; soluble mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1; sST2, soluble IL-1 receptor-like 1; TME, tumour microenvironment.