Figure 1.
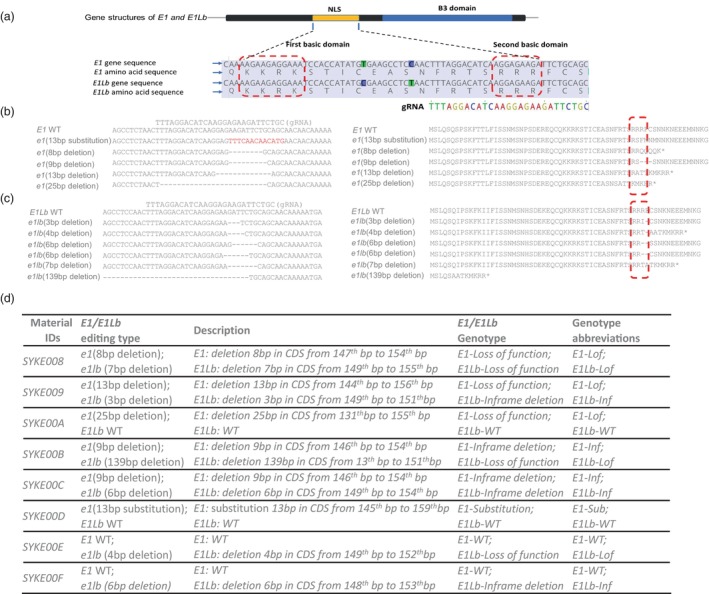
E1/E1Lb gRNA design, E1 mutations and E1Lb mutations, genotype of eight selected edited lines with different E1/E1Lb mutation combinations. (a) Gene structures of E1/E1Lb and gRNA target site. Gene structure of E1 and E1Lb, including putative bipartite NLS region and B3 domain. Two basic domains of NLS are conversed in both E1 and E1Lb. The gRNA was designed at second basic domain of NLS region in both E1 and E1Lb. The red box highlights the first and second basic domain of NLS. The coloured sequence is gRNA, and TTTA is the PAM of gRNA. (b) Gene sequence and amino acid sequence of the E1 mutations at gRNA target region in T2 homo edited lines. Minus represents deletion, and nucleotides in red indicate substitution. The amino acids in the red boxes show the changes that occurred at the second basic domain of NLS after editing. (c) Gene sequence and amino acid sequence of E1Lb mutations at gRNA target region in T2 homo edited lines. Minus represents deletion. The amino acids in the red boxes show the changes that occurred at the second basic domain of NLS after editing. (d) The genotype of the final eight selected edited lines in the T2 generation after segregation. Lof is the abbreviation for loss of function caused by non‐multiples three base pair deletion; Inf is the abbreviation for in‐frame deletion mutations that represents three or multiple three base pair deletion; and Sub is the abbreviation for a substitution mutation that represents base pair substitution.
