Figure 3.
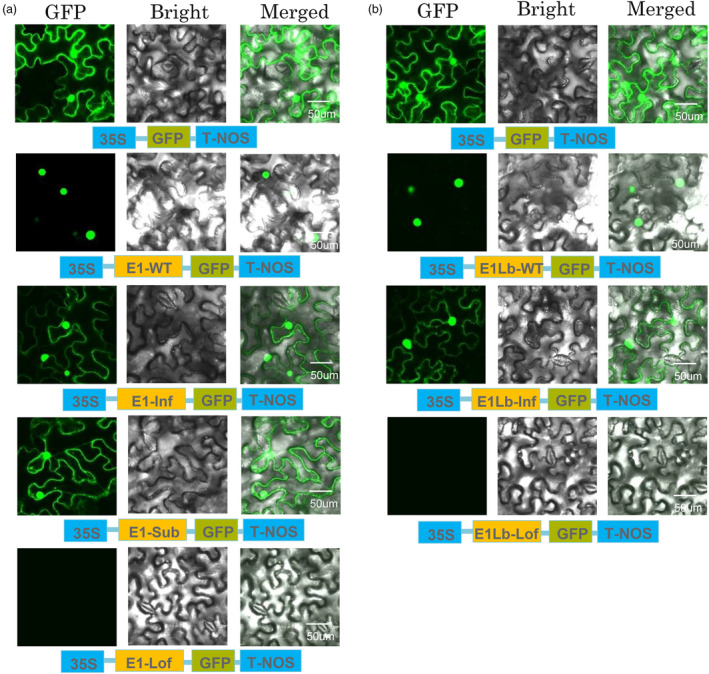
Subcellular localization of GFP and of the E1‐WT, E1‐Substitution, E1‐Inframe deletion, E1‐Loss of function, E1Lb‐WT, E1Lb‐Inframe deletion and E1Lb‐Loss of function fusion proteins. (a) Subcellular distribution of the E1 and E1 mutation proteins in tobacco epidermal cells. E1‐GFP, E1‐Sub‐GFP, E1‐Inf‐GFP and E1‐Lof‐GFP fusion proteins were produced transiently under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter and T‐Nos in tobacco epidermal cells and were observed under a confocal microscope. E1‐GFP protein was only distributed in nuclei, but E1‐Sub‐GFP and E1‐Inf‐GFP were distributed in both nuclei and cytoplasm. Moreover, no E1‐Lof‐GFP was detected. (b) Subcellular distribution of the E1Lb and E1Lb mutation proteins in tobacco epidermal cells. E1Lb‐GFP, E1Lb‐Inf‐GFP and E1Lb‐Lof‐GFP fusion proteins were produced transiently under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter and T‐Nos in tobacco epidermal cells and were observed under a confocal microscope. E1Lb‐GFP protein only distributed in nuclei, but E1‐Inf‐GFP distributed in both nuclei and cytoplasm. And no E1Lb‐Lof‐GFP was detected. The photographs were taken with a dark field for green fluorescence (left), with a bright field for the cell morphology (centre) and with a combination approach (merged, right). In a and b, the experiments were performed three times, with similar results obtained.
