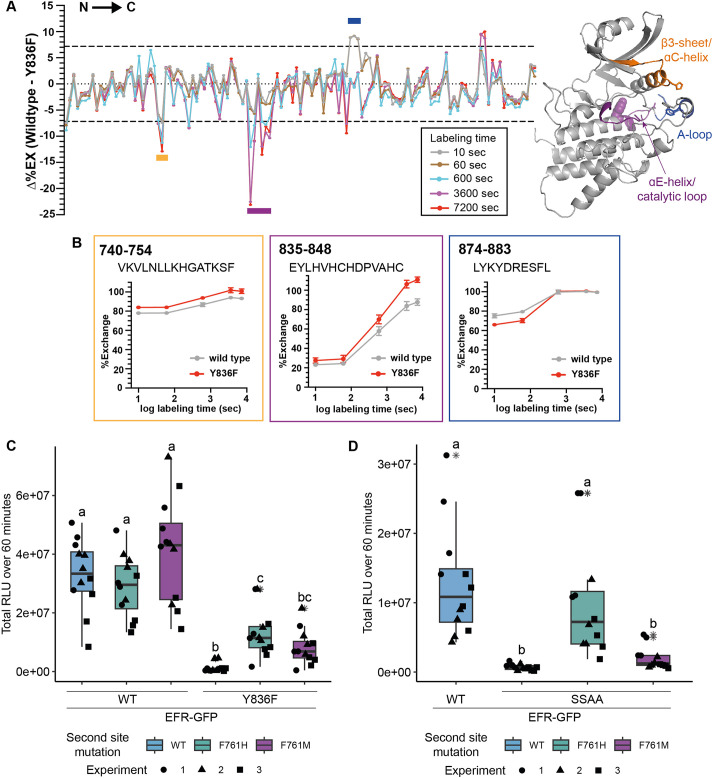
Figure 2. EFRY836F and EFRSSAA impair the active kinase conformation, which is required for signaling function.
(A) (left) HDX-MS results for unphosphorylated EFR and EFRY836F protein. The difference in percent H/D exchange in wild type EFR and EFRY836F is expressed as the Δ%EX (wild type EFR – EFRY836F), with the positive and negative Δ%EX indicating more stabilized and destabilized regions in EFRY836F, respectively, compared to wild-type EFR. The Δ%EX values at different labeling time points are shown as colored lines, as indicated in the figure. The horizontal dotted black lines indicate the 98% confidence interval for the Δ%EX data (±7.18%, corresponding to ±0.4 Da difference between wild type and Y836F percent exchange) calculated as described previously (Houde et al., 2011). Regions with Δ%EX values that exceed this confidence limit are indicated as colored bars in the figure, including the β3-αC loop (orange), the catalytic loop plus part of αE (purple), and the A-loop (blue). These regions are colored in the AlphaFold2-derived model of the EFR kinase domain shown at right, in which Y836 is shown as a purple sphere. All data are the average of three independent biological repeats (n=3) with three technical repeat experiments each. A summary of the HDX-MS analysis is presented in Table 3. (B) HDX-MS analysis of representative peptides from regions with significantly different HD exchange. Frames are color-coded according to regions in A. Amino acid range of the peptides in full length EFR are indicated in the top left corner and the sequence below. (C, D) Secondary site mutation EFR F761[H/M] partially restores function of EFRY836F (C) and EFRSSAA (D). Full length EFR and its variants were expressed transiently in N. benthamiana and their function was tested in an oxidative burst assay. EFR F761H partially restored oxidative bursts of EFRY836F and EFRSSAA. Outliers are in indicated by asterisk in addition to the outlier itself and are included in statistical analysis; Statistical test: Kruskal-Wallis test (p<2.2*10–16 in C, p=1.163*10–7 in D), Dunn’s post-hoc test with Benjamin-Hochberg correction (p ≤ 0.05) Groups with like lowercase letter designations are not statistically different.