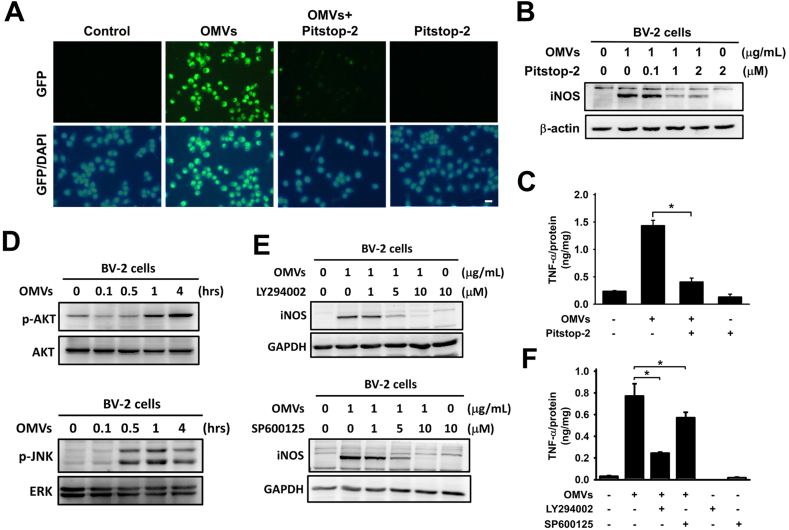
Figure 5.
Pg-OMVs-mediated microglial activation is dependent on endocytosis and AKT and JNK signaling pathways. (A) The BV-2 cells were pretreated with Pitstop (2 μM) for 30 min and then incubated with DiO3-labeled Pg-OMVs (green) for another 24 h. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Western blot analysis of the levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in BV-2 cells pretreated with Pitstop (2 μM) for 30 min and then incubated with Pg-OMVs (1 μg/mL) for 24 h. (C) ELISA analysis of TNF-α production in BV-2 cells exposed to Pg-OMVs and Pitstop. The levels of TNF-α were normalized to total protein. The bar represents the mean ± SEM of three different experiments (∗P < 0.05). (D) Western blot analysis of pAKT and pJNK production in BV-2 cells exposed to Pg-OMVs (1 μg/mL) for the indicated time. (E) Western blot analysis of the levels of iNOS in BV-2 cells pretreated with different concentrations of AKT inhibitor LY294002 and JNK inhibitor SP600125 for 30 min and then incubated with OMVs (1 μg/mL) for 4 h. (F) ELISA analysis of TNF-α production in BV-2 cells exposed to Pg-OMVs and AKT and JNK inhibitors. The levels of TNF-α were normalized to total protein. The bar represents the mean ± SEM of three different experiments (∗P < 0.05).