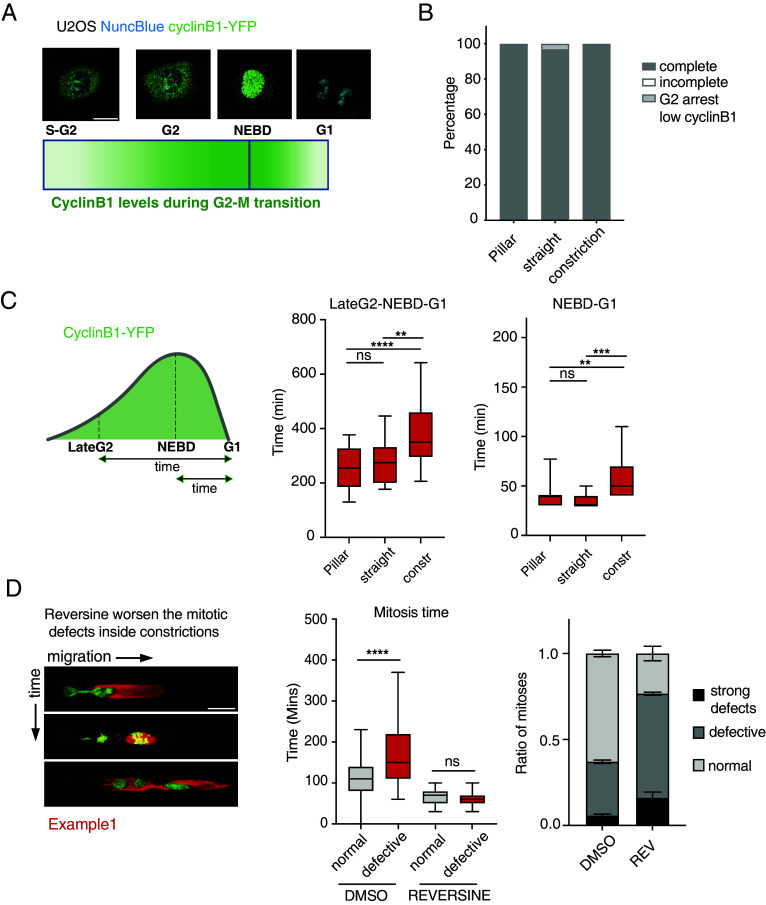
Fig. 2.
Confined migration causes defective mitosis and aneuploidy in spite of a functional SAC. (A) Schematic representation of cyclinB1 expression during cell cycle along with example images from U2OS Cyclin B1-YFP cells where DNA was stained using the NuncBlue dye. Cyclin B1-YFP fluorescence signal increases at the end of S-phase and continues to show higher intensity though G2-phase until mitosis. Upon NEBD cyclin B1 enters the nucleus and is decayed as the sister chromatids separate into daughter cells. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (B) Analysis of mitotic events in U2OS cells expressing Cyclin B1-YFP and migrating outside or inside microchannels. (C) Analysis of cyclin B1-YFP lifespan during mitosis in U2OS cells migrating inside channels. Cyclin B1-lifespan is increased in U2OS cells dividing inside constrictions (LateG2-G1) suggesting a mitotic stress. Mitosis inside constrictions also causes a mild delay in cyclin B1 degradation following NEBD in U2OS cells (NEBD-G1). ****P value < 0.0001, **P value < 0.01 ***P value < 0.001 one-way ANOVA. (D) Time-lapse images showing increased mitotic defects in U2OS H2B-GFP Tubulin-mCherry cells dividing inside microchannels (Left). Reversine abolishes the mitotic delay in U2OS H2B-GFP Tubulin-mCherry cells undergoing defective mitoses during interstitial migration suggesting that SAC is activated by chromosome missegregations caused by mechanical stress. Mitotic time is measured as the time-window between chromosome condensation in prophase and the generation of G1 daughter cells (Central graph). Reversine 0.5 μM treatment significantly worsens the mitotic defects in U2OS H2B-GFP Tubulin-mCherry cells dividing inside microchannels (Right graph). ****P value< 0.0001 one-way ANOVA. Error bars in the bar graph are SDs.