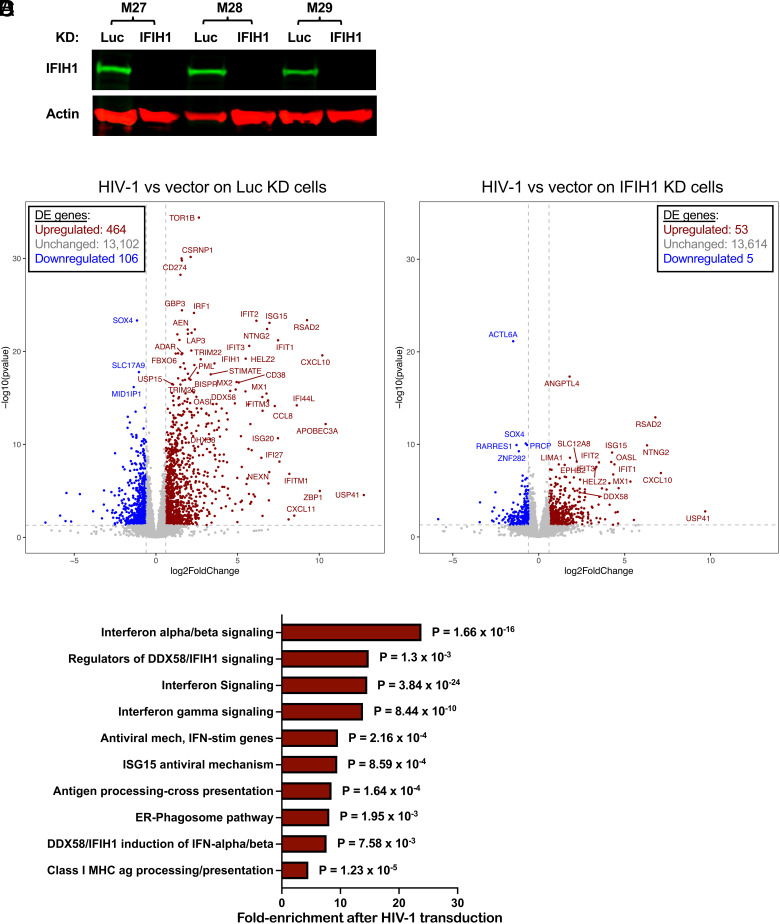
Fig. 7.
Effect of HIV-1 transduction and of IFIH1 knockdown on the dendritic cell transcriptome. CD14+ monocytes from three blood donors (coded M27, M28, and M29) were transduced with shRNA-puromycin resistance vectors targeting either IFIH1 or Luc control, as indicated. Cells were selected with puromycin for 3 d, and differentiated into dendritic cells. (A) Immunoblot shows steady-state levels of IFIH1 (MDA5) protein for the indicated samples. Then, dendritic cells were either transduced with HIV-1-GFP or left untransduced. At 48 h, RNA was isolated from cells, and poly(A)-selected libraries were generated for RNA-Seq. Volcano plot depicting differentially expressed genes after HIV-1 challenge in Luc knockdown control cells (B), or in IFIH1-knockdown cells (C), as determined by DESeq2 combining RNA-Seq data from the three blood donors. Red dots indicate genes with log2 fold change of normalized counts >1; P < 0.01. Blue dots indicate the log2 fold change of normalized counts <−1; P < 0.01. Gray dots failed to achieve either criterion. (D) Reactome pathway analysis based on 276 differentially expressed genes in HIV-1 transduced Luc-knockdown cells in comparison to HIV-1 transduced IFIH1-knockdown cells. Gene Ontology-produced P values (as determined by Fisher’s exact test) with FDR correction (Benjamini–Hochberg method) are shown. SI Appendix, Tables S1 and S2 show differentially expressed genes in B and C, respectively.