Fig. 3 |. Overview of single-cell multi-omic assays for genomic profiling and the co-detection of mtDNA mutations.
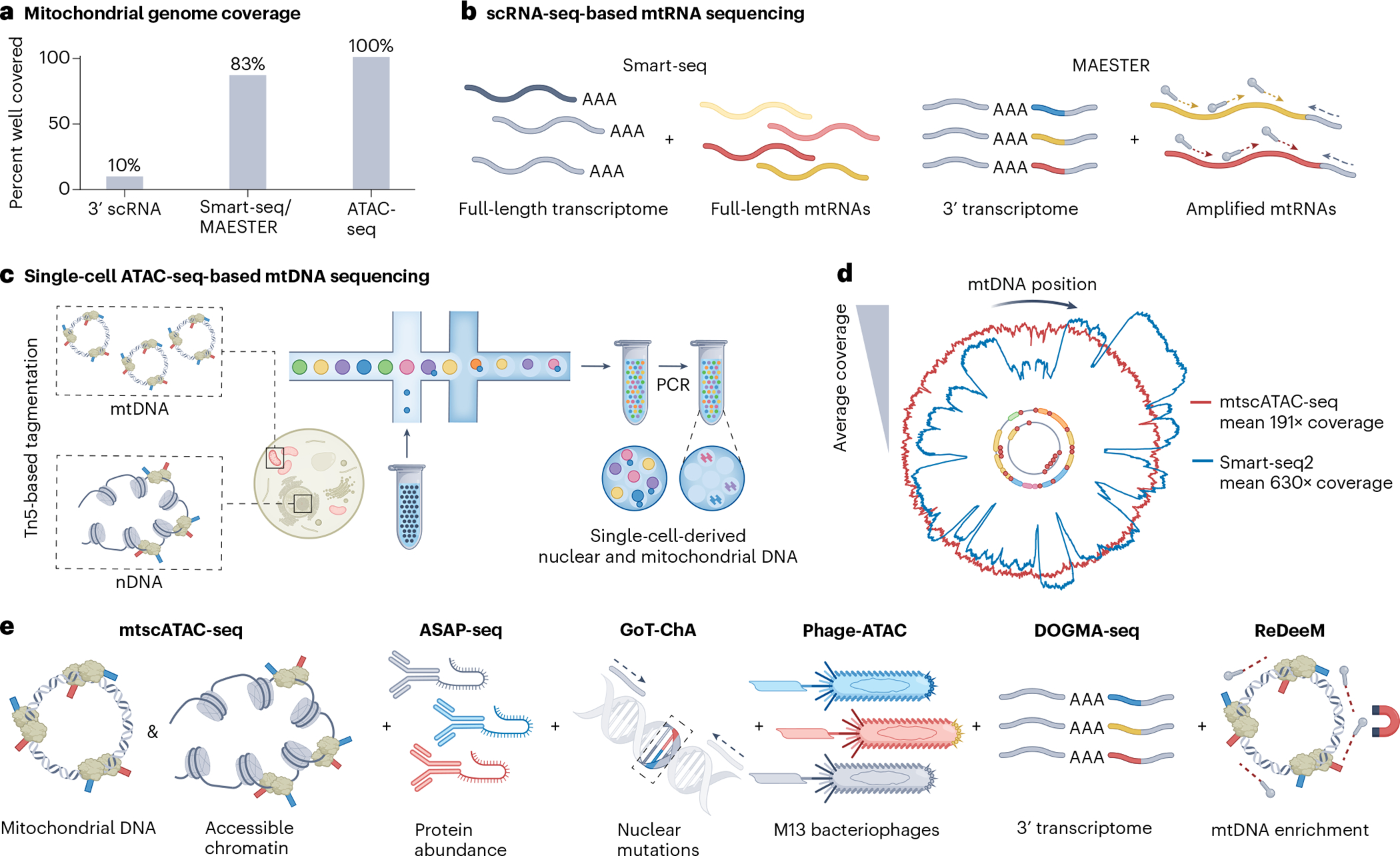
a, Several single-cell omics assays inherently capture mtDNA or may be modified to do so, but cover mtDNA sequences to different degrees, with ATAC-seq-based assays showing the highest mitochondrial genome coverage. b, Among the full-length RNA sequencing approaches, Smart-seq uses poly(A)-based priming to capture large fractions of the mitochondrial transcriptome, including rRNAs, but not tRNAs (left). scRNA-seq techniques can be augmented via the tiling of primers across mitochondrial transcripts to increase mtRNA variant coverage as done in MAESTER (right). c, Schematic illustration of droplet-based encapsulation of cells in mtscATAC-seq. As mtDNA is not densely packed, it is thus readily accessible to tagmentation, analogous to regions of accessible chromatin (left). Following bulk Tn5 tagmentation of cells, individual cells may be droplet-encapsulated (middle), after which PCR enables the amplification of accessible nuclear and mtDNA fragments from single cells (right) for genome-wide mtDNA variant identification in combination with profiling of accessible chromatin. d, Mitochondrial genome coverage is variable depending on technology and type of oligonucleotide (mtDNA for mtscATAC-seq and mtRNA for Smart-seq2) used, as exemplified here for the hematopoietic TF1 cell line. For example, dips in coverage for Smart-seq relate to the inability to capture mitochondrial tRNA, which is not polyadenylated. Note that coverages may differ substantially by cell type. e, Schematic illustration of approaches for single-cell mtDNA genotyping based on mtscATAC-seq (left) that can be variably combined with different genomic readouts (to the right). Antibody-mediated protein marker profiling is enabled by ASAP-seq. Phage-ATAC leverages nanobodies displayed on phagemids to quantify protein markers. The GoT-ChA assay co-detects nDNA mutations using targeted primers. DOGMA-seq enables additional transcriptome profiling, by combining mtscATAC-seq with scRNA-seq. However, mitochondrial genome coverage is less pronounced compared to the standalone mtscATAC-seq assay, leading to the development of ReDeeM, which experimentally enriches mtDNA during library preparation. See Box 1 for further details on the different methods. Panel c adapted from ref. 91, Springer Nature Limited, panel d adapted with permission from ref. 28, Elsevier.
