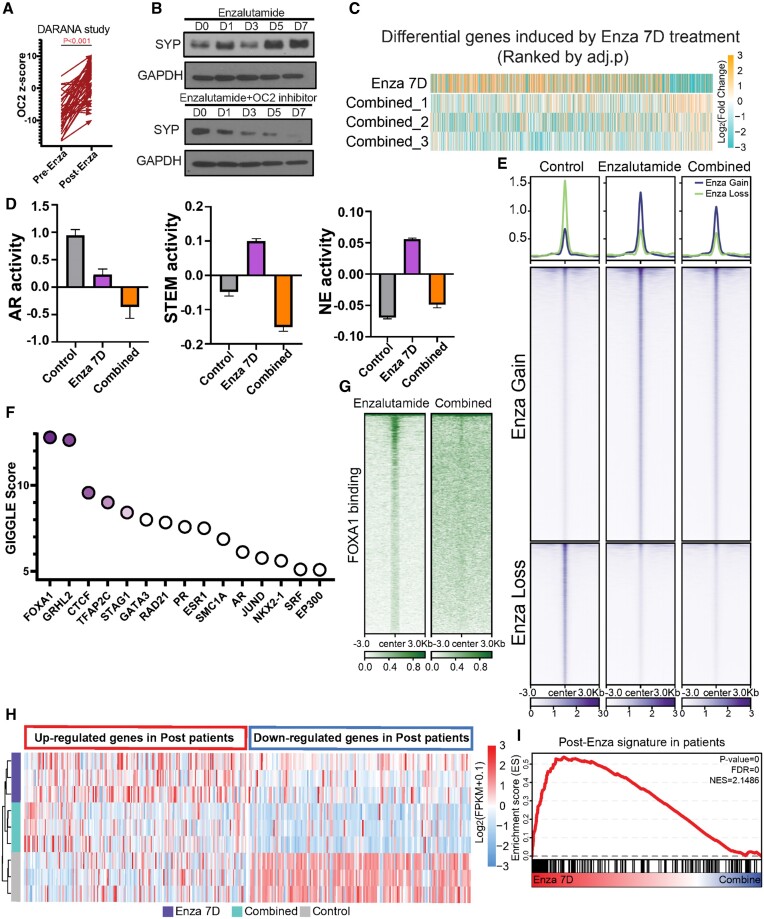
Figure 7.
OC2 inhibition suppresses lineage plasticity evoked by enzalutamide. (A) Pre- and post-enzalutamide treatment in the same patients showed OC2 activation following ARSI therapy (GSE197780). (B) OC2 inhibitor blocks enzalutamide-induced SYP expression in LNCaP cells. (Enzalutamide: 10uM; OC2 inhibitor: 10 uM). (C) Simultaneous combination (Combined) treatment of OC2 inhibitor with enzalutamide broadly suppressed enzalutamide-induced gene expression changes versus control. (D) AR, Stem and NE lineages were repressed by combined treatment with OC2 inhibitor. Heatmap of gene expression in these three lineages is shown. Non-expressing genes were removed from the heatmap. (E) Combined treatment with OC2 inhibitor greatly suppressed enzalutamide-induced chromatin accessibility changes (enzalutamide: 10 uM; OC2 inhibitor: 10 uM). (F) GIGGLE analysis identified FOXA1 as the most enriched TF in suppressed hyper-accessible regions of combination treatment versus enzalutamide alone. (G) FOXA1 CUT&RUN-seq showed combined treatment with OC2 inhibitor suppressed FOXA1-driven chromatin accessibility changes. (H-I) A gene signature derived from post-enzalutamide patient samples was consistent with perturbed genes seen in enzalutamide-treated LNCaP cells. SC treatment with OC2 inhibitor blocked enzalutamide-induced gene perturbation.