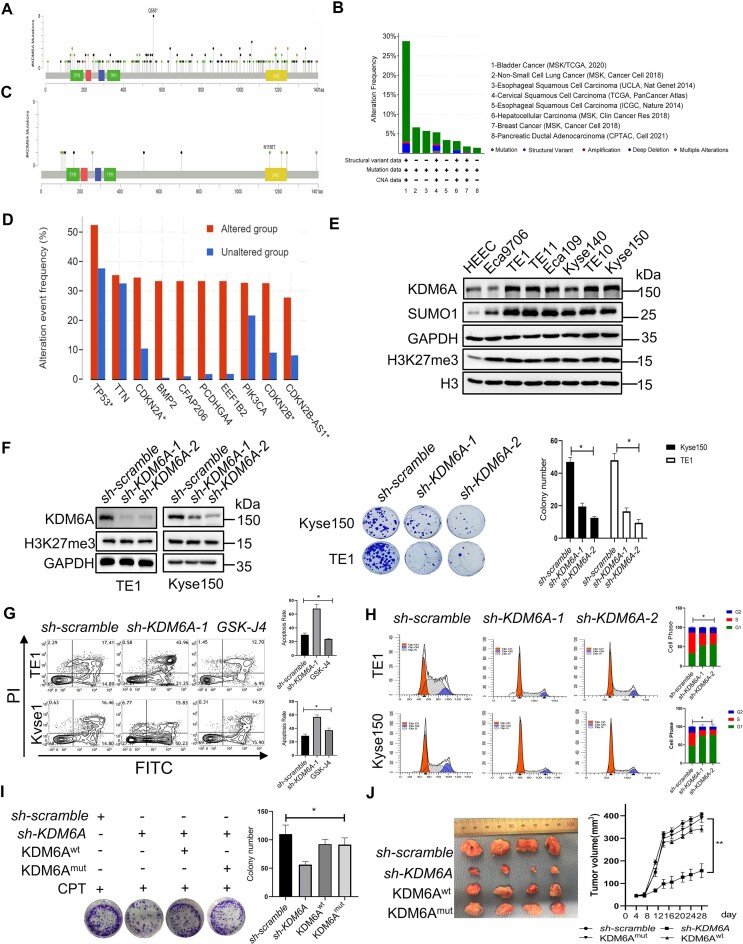
Figure 8.
Loss of KDM6A increases the sensitivity of ESCC toward CPT. (A–D) KDM6A mutations and expression in tumors was analyzed using data from public database Cbioportal. (E) Western blot of KDM6A expression in ESCC cells. The lysate was prepared from ESCC cells including Eca9706, Eca109, TE1, TE10, TE11, Kyse140, Kyse150 and was subjected to western blot with indicated antibodies. (F) Cellular viability for indicated ESCC cells with KDM6A knockdown in the presence of genotoxin CPT (Middle panel). Quantification of colony formation was shown (Right panel). KDM6A knockdown was validated by western blot (Left panel). (G, H) Apoptosis of ESCC cells lacking KDM6A in response to CPT (G) and cell cycle profile of ESCC cells without CPT treatment (H). (I) Cellular viability for ESCC cells knocked down endogenous KDM6A and followed by transfection with the plasmid of KDM6Awt or catalytic-dead KDM6Amut respectively. Quantification of colony formation was shown (Right panel). (J) Inhibition of tumorigenesis in vivo by knocking KDM6A down. Xenograft was generated using ESCC cells same as it in panel H (left panel), and tumor size was measured at the end of the study (right panel). Data represent mean ± S.E.. All experiments were repeated for three times independently, *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01.